Figure 3.
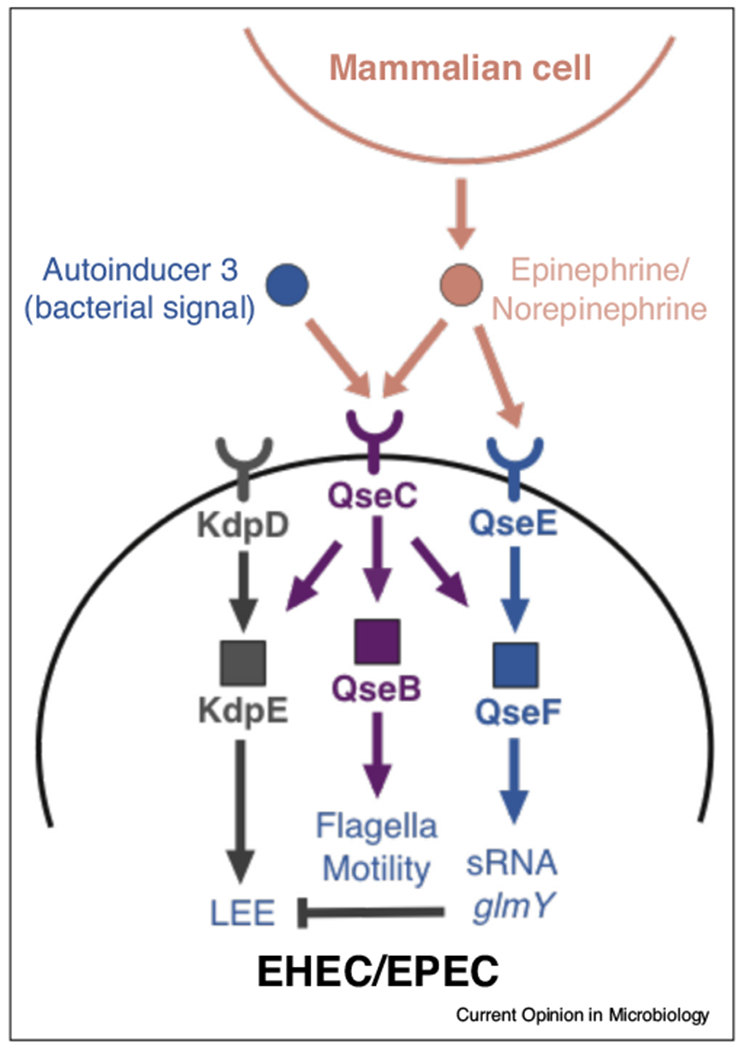
The QseC quorum sensing system in pathogenic Escherichia coli. A major quorum sensing response system in E. coli consists of a two-component system comprises the histidine sensor kinase (HK) QseC and its cognate response regulator (RR) QseB. The QseC receptor is autophosphorylated upon engagement with the QS signal autoinducer-3 and then transfers the phosphate to QseB, which transcriptionally stimulates flagella biosynthesis. QseC, along with a second HK QseE, also sense the host neurotransmitters epinephrine and norepinephrine. Kinase activity in QseC is promiscuous and can activate two additional non-cognate RRs, KdpE and QseF. In enterohemorrhagic and enteropathogenic E. coli (EHEC, EPEC), QseC also regulates the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE), which is essential for causing intestinal disease. In EHEC and EPEC, QseC activates the LEE through KdpE, a positive regulator of the LEE, and inhibits the LEE through sRNAs that are modulated by QseF.
