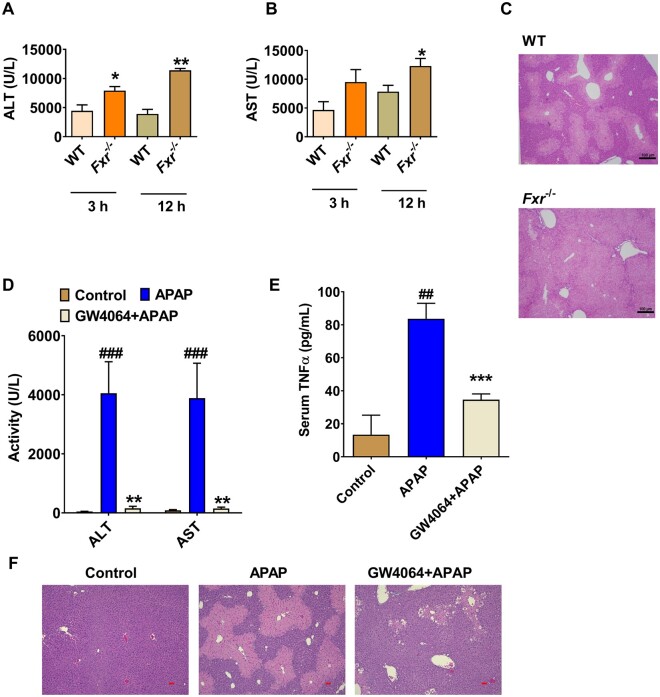
Figure 1.
GW4064 protects, while farnesoid X receptor (FXR) deficiency enhances, acetaminophen (APAP) -induced liver injury in mice. A and B, Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST)levels at 3 or 12 h after APAP dosing in global Fxr−/− mice and wild-type (WT) mice. C, Liver hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining for WT mice and Fxr−/− mice at 12 h after APAP treatment, scale bar 100 µm. D, Serum ALT and AST levels. E, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α levels in control or GW4064-treated mice. F, Liver H&E staining for GW4064/APAP-treated mice at 24 h after APAP dosing, scale bar 50 µm (n = 5 mice per group). Data are presented as means ± SEM. *p < .05 and **p < .01 compared with WT group or GW4064-treated group. ###p < .005 compared with Control group. WT mice treated with 200 mg/kg of APAP. Fxr−/−, Fxr-null mice treated with 200 mg/kg of APAP. Vehicle + APAP, APAP-dosed mice pretreated with vehicle; GW4064, APAP-dosed mice pretreated with GW4064; Control, control saline-treated mice.