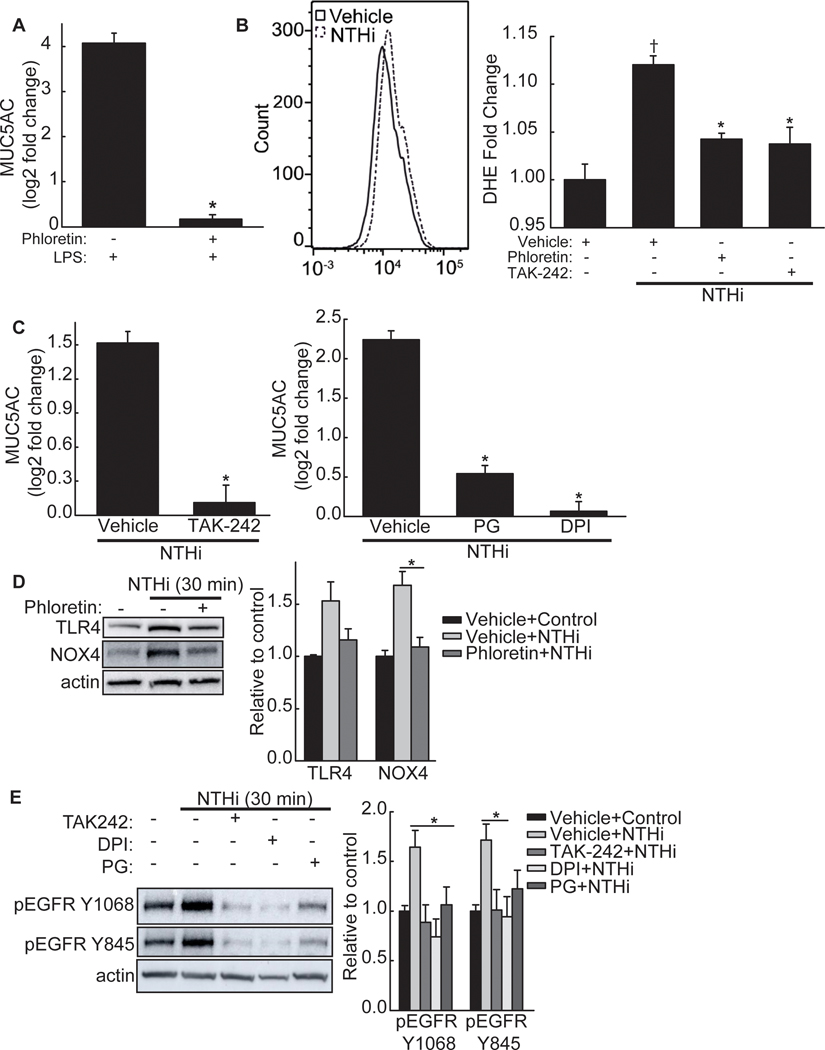
Figure 2. Phloretin inhibits NTHi-induced phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-MAPK pathway through toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) signaling.
A. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces mucin 5AC, oligomeric mucus/gel-forming (MUC5AC) mRNA in NCI-H292 cells, which is inhibited by phloretin. NCI-H292 cells were treated without or with 100 μM phloretin and exposed to 1 μg/mL LPS (24 h). MUC5AC and RPL32 mRNA was measured by RT-qPCR. Values (mean ± SEM, n=9) are log2 fold change of MUC5AC mRNA normalized to RPL32 relative to vehicle control treated cells. *Significantly different (p<0.05) in LPS + phloretin compared to LPS alone treated cells, as determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison method. B. NTHi increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in NCI-H292 cells, which is inhibited by phloretin and a TLR4 inhibitor, TAK-242. NCI-H292 cells were exposed to vehicle, 100 μM phloretin, or 30 μM TAK-242 (1 h) and stimulated with NTHi (30 min). Intracellular ROS production was detected by phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated dihydroethidium (DHE) using flow cytometry (excitation 488 nm, emission 585 nm). (Left Panel) Representative result (10,000 cells) of increased fluorescence following NTHi treatment (dash line) compared to control (solid line). (Right Panel) Fluorescence intensity (mean ± SEM, n=4) of vehicle alone, NTHi, NTHi + phloretin, and NTHi + TAK-242 treated cells. †Significantly different (p<0.05) from vehicle control as determined by ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison method. *Significantly different (p<0.05) from NTHi treated cells as determined by ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison method. C. Inhibition of TLR4 and ROS reduces NTHi-induced MUC5AC mRNA. NCI-H292 cells were incubated (1h) with (Left Panel) 30 μM TAK-242 or (Right Panel) 10 μM diphenyleneiodonium (DPI), a NADPH oxidase inhibitor, or 100 μM propyl gallate (PG), a ROS scavenger, and stimulated with NTHi (8h). MUC5AC and RPL32 mRNA were measured by RT-qPCR. Values (mean ± SEM, n=9–18) are log2 fold change of MUC5AC normalized to RPL32 relative to vehicle control treated cells. *Significantly different (p<0.05) from NTHi treated cells as determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison method. D. NTHi increases TLR4 and NOX4 protein, which phloretin inhibits. NCI-H292 cells were pretreated with vehicle or 100 μM phloretin (1 h) and exposed to NTHi (30 min). (Left Panel) Cell protein extract was collected and immunoblotted with anti-TLR4, anti-NOX4, or anti-β-actin antibodies. (Right Panel) Values (mean ± SEM, n=4) are fold change in protein expression relative to vehicle control normalized to the β-actin control. *Significantly different (p<0.05) from NTHi treated cells as determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons method. E. Inhibition of TLR4 and ROS inhibits NTHi-induced EGFR phosphorylation. NCI-H292 cells were pretreated with TAK-242, DPI, or PG (1 h) and exposed to NTHi (30 min). (Left Panel) Cell protein extract was collected and immunoblotted for phosphorylated EGFR (anti-Y1068 or anti-Y845) or anti-β-actin. (Right Panel) Values (mean ± SEM, n=4) are fold change in protein expression relative to vehicle control normalized to the β-actin control. *Significantly different (p<0.05) from NTHi treated cells as determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons method. Tests were performed on ≥2 occasions.