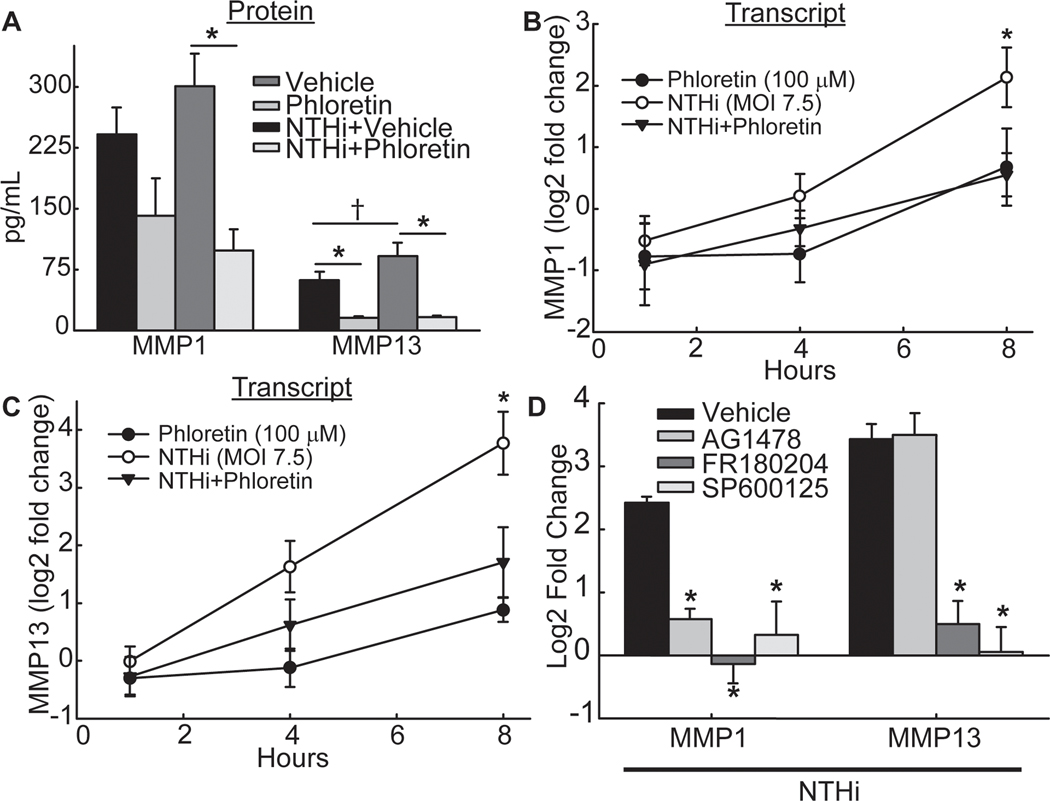
Figure 4. Phloretin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) production stimulated by NTHi induced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling.
A. Phloretin decreases baseline levels of MMP13 protein and NTHi-induced MMP1 and MMP13 protein. NCI-H292 cells were pretreated without or with 100 μM phloretin (1 h) and exposed to NTHi (8 h). Secreted MMP1 and MMP13 protein were measured in cell supernatant by Luminex multiplex assay. Values (mean ± SEM, n = 9–10) are protein concentration (pg/mL). †Significant difference (p<0.05) between vehicle and NTHi-treated cells as determined ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons method. *Significantly different (p<0.05) from NTHi treated cells, as determined ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak multiple comparison method. B. Phloretin inhibits NTHi-induced increased MMP1 transcript. NCI-H292 cells were pretreated without or with 100 μM phloretin (1 h) and exposed to NTHi (1, 4, and 8 h). MMP1 and RPL32 transcripts were measured by RT-qPCR. Values (mean ± SEM, n =8–9) are log2 fold change of MMP1 mRNA normalized to RPL32 relative to vehicle control treated cells. *Significantly different (p<0.05) in NTHi compared to vehicle control treated cells, as determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons method. C. Phloretin inhibits NTHi-induced increased MMP13 transcript. NCI-H292 cells were pretreated without or with 100 μM phloretin (1 h) and exposed to NTHi (1, 4, and 8 h). MMP13 and RPL32 transcripts were measured by RT-qPCR. Values (mean ± SEM, n=8–9) are log2 fold change of MMP13 mRNA normalized to RPL32 relative to vehicle control treated cells. *Significantly different (p<0.05) in NTHi compared to vehicle control treated cells, as determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons method. D. Inhibition of MMP1 is through the EGFR-MAPK pathway whereas inhibition of MMP13 is through MAPK signaling. NCI-H292 cells were pretreated (1 h) with 1 μM AG-1478, an EGFR inhibitor, 30 μM FR180204, a MAPK3/1 inhibitor, or 100 μM SP600125, a MAPK8 inhibitor, and exposed to NTHi (8 h). MMP1, MMP13 and RPL32 transcripts were measured by RT-qPCR. Values (mean ± SEM, n=6–12) are log2 fold change of MMP1 and MMP13 mRNA normalized to RPL32 relative vehicle control treated cells. *Significantly different (p<0.05) from NTHi treated cells, as determined by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons method. Tests were performed on ≥2 occasions.