Fig. 4. Changes in neuropeptide expression in the SCN.
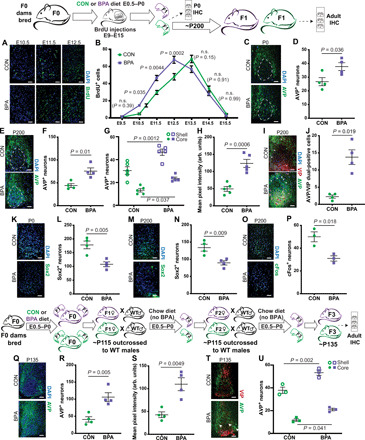
BPA exposure increases early (E10 to E12) SCN neurogenesis [representative images from the significantly changed time points shown in (A) and quantification in (B), two-way ANOVA, P values compare treatments at each time point], increases AVP+ neurons in P0 [representative images in (C) and quantification in (D)], and adult animals relative to controls [representative images in (E) and quantification in (F)]. This was consistent when the shell and core were counted separately (G) (two-way ANOVA), and total AVP expression was also higher in BPA animals (H). AVP and VIP costaining revealed a BPA-mediated increase in AVP/VIP dual-positive neurons [representative images in (I) and quantification in (J), white arrows mark sample shell AVP+ cells, and pink arrows mark dual-positive cells in BPA sections]. SCN Sox2+ cells were reduced in BPA mice at P0 [representative images in (K) and quantification in (L)] and adult mice [representative images in (M) and quantification in (N)]. BPA exposure reduced light-induced cFos expression [representative images in (O) and quantification in (P)]. BPA-exposed F3 mice also had less SCN AVP+ neurons [representative images in (Q) and quantification in (R)] and lower overall expression (S). F3 mice also displayed the same change in region-specific AVP+ neurons [representative images in (T) and quantification in (U), two-way ANOVA]. (Where appropriate, dashed line delineates the SCN core).
