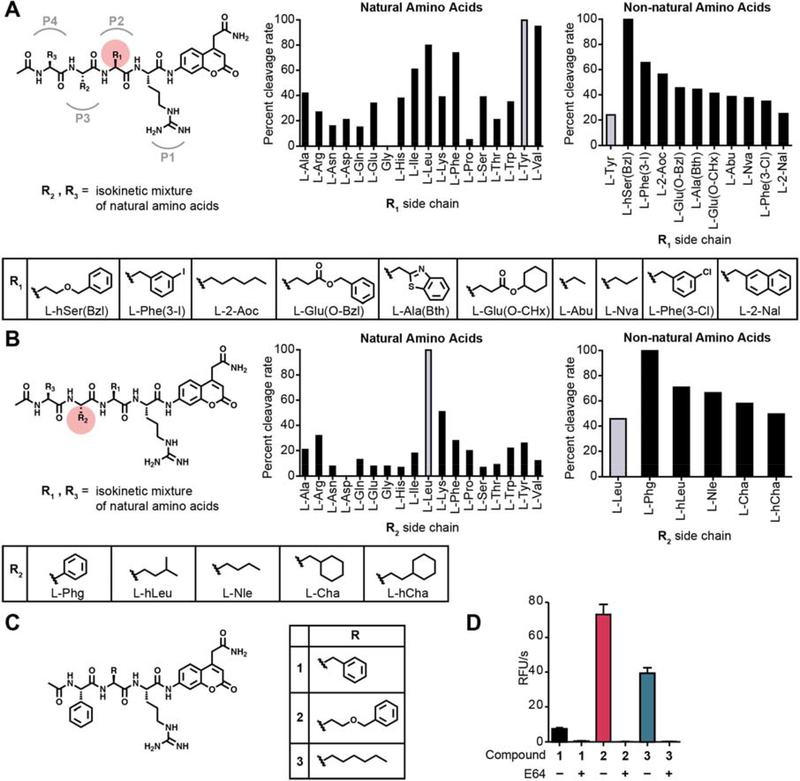
Fig. 1. Proteolytic profiling of whole murine tumor tissue lysate with non-natural amino acid libraries.
(A) Screening of the P2 scanning HyCoSuL library in mouse tumor tissue extract. The library contains arginine in P1, a variety of natural and non-natural amino acids in P2, and an isokinetic mixture of natural amino acids in P3 and P4. Plot of ACC cleavage relative to the most effectively cleaved residue is shown for natural amino acids (left) and the top non-natural amino acids with activity above the most optimal natural amino acid (right). Mean values of two tumor measurements were used. Structures of the non-natural amino acids from the plots are shown below. (B) Screening of the P3 scanning HyCoSuL library in mouse tumor tissue extract. The P3 scanning library was assayed exactly as in (A). (C) Structures of the ACC peptide substrates (1–3) synthesized based on optimal residues identified from the HyCoSuL screen in (A) and (B). (D) Plot of cleavage velocity of ACC substrates 1–3 in 4T1 murine breast cancer lysates with and without preincubation with cysteine cathepsin inhibitor E64 (10 μM). Mean value ± SD are plotted. n= 3.