FIGURE 4.
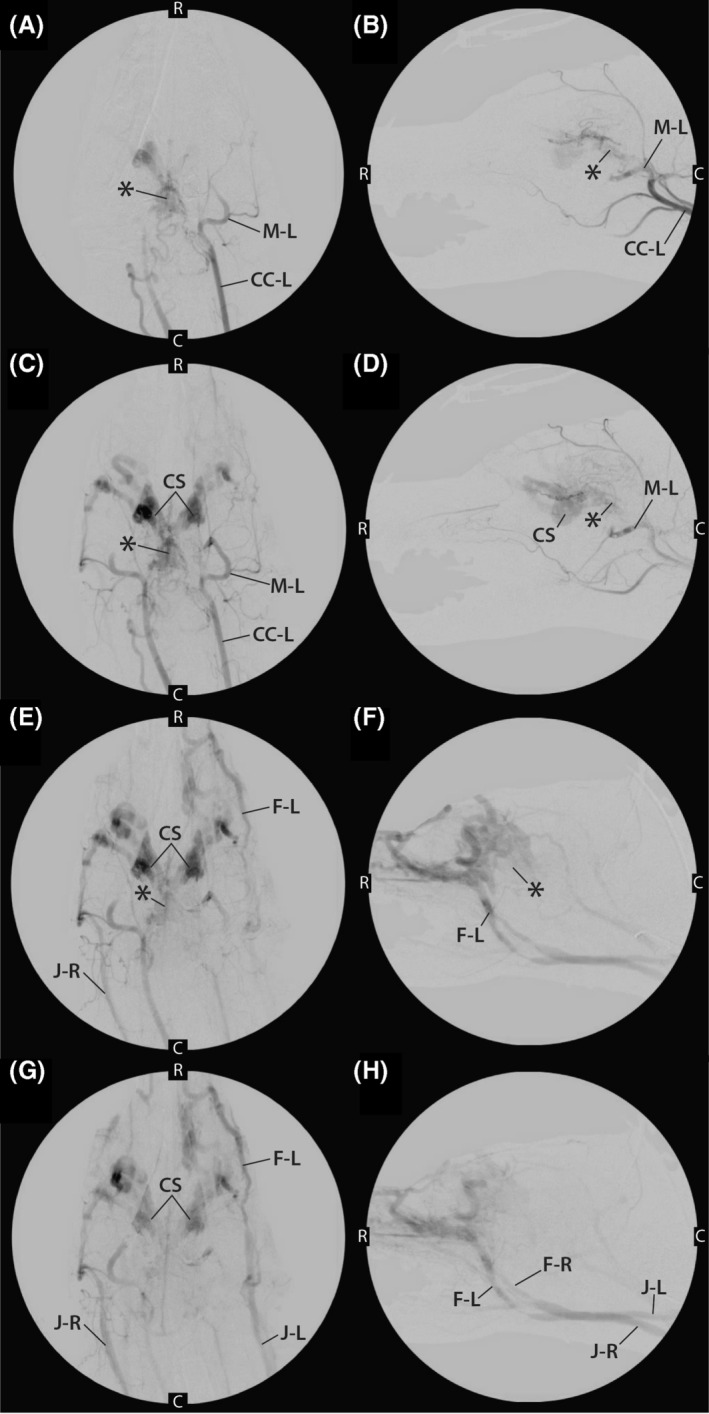
A,B, Early phase angiograms performed from injection of contrast medium into left common carotid artery (CC‐L) in both dorsal (A) and lateral (B) recumbency. During this injection, the contrast enhancement of the left maxillary artery (M‐L) and AVM nidus (*) can be visualized. C, caudal; R, rostral. C,D, mid‐phase angiogram after injection of contrast medium into left common carotid artery (CC‐L) in both dorsal (C) and lateral (D) recumbency. The left maxillary artery (M‐L) and AVM nidus (*) can still be seen as can the cavernous sinus (CS). C, caudal; R, rostral. E,F, Late‐phase angiogram after injection of contrast medium into left common carotid artery in both dorsal (E) and lateral (F) recumbency. At this point, contrast enhancement of the nidus (*) is only faintly identified, and contrast medium is clearing from the CS and draining into the left facial vein (F‐L) and right jugular vein (J‐R). C caudal; R, rostral. G,H, Late‐phase angiogram after injection of contrast medium into the left common carotid artery in both dorsal (G) and lateral (H) recumbency. Bilateral venous drainage of the contrast medium can be visualized after contrast medium has passed through the AVM. The CS, left facial vein (F‐L), right facial vein (F‐R), left external jugular vein (J‐L), and right external jugular vein (J‐R) are visualized. C caudal; R, rostral
