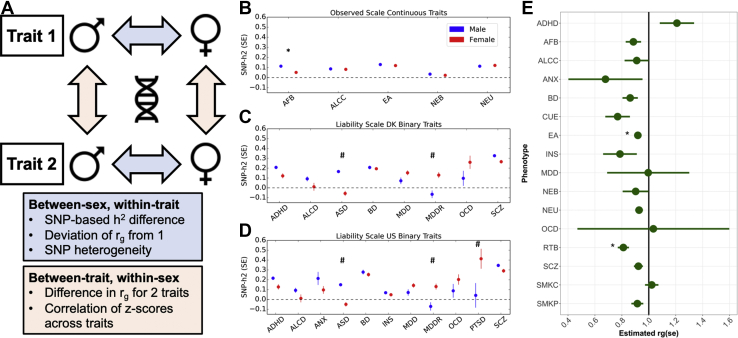
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic illustration of the key analyses used to investigate between-sex, within-trait and between-trait, within-sex differences. (B–D) Estimates of sex stratified SNP-based heritability (SNP-h2) on (B) the observed scale for continuous traits and the liability scale using population prevalence based on (C) Denmark (DK) and (D) the United States (US). Estimates were obtained from linkage disequilibrium score regression. Points represent the estimated SNP-h2 in males (blue) and females (red), while bars represent SE of the SNP-h2 estimates. Significant sex difference in heritability is denoted as follows: ∗p < .0042 (adjusted p value threshold corrected for multiple testing using Bonferroni). #Traits for which significance in difference is not interpretable owing to negative or nonsignificant from zero SNP-h2 value for one of the measurements. (E) Within-trait, between-sex genetic correlation (rg) estimates using linkage disequilibrium score regression. Points represent the estimated rg, and bars represent SE of the rg estimates. Significant deviation from 1 is denoted as follows: ∗p < .0031 (adjusted p value threshold corrected for multiple testing using Bonferroni). ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; AFB, age at first birth; ALCC, alcohol use; ALCD, alcohol dependence; ANX, anxiety disorders; ASD, autism spectrum disorder; BD, bipolar disorder; CUE, cannabis use (ever); EA, educational attainment; INS, insomnia; MDD, major depressive disorder; MDDR, major depressive disorder recurrent; NEB, number of children ever born; NEU, neuroticism; OCD, obsessive-compulsive disorder; PTSD, posttraumatic stress disorder; RTB, risk-taking behavior; SCZ, schizophrenia; SMKC, smoking (current); SMKP, smoking (previous); SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.