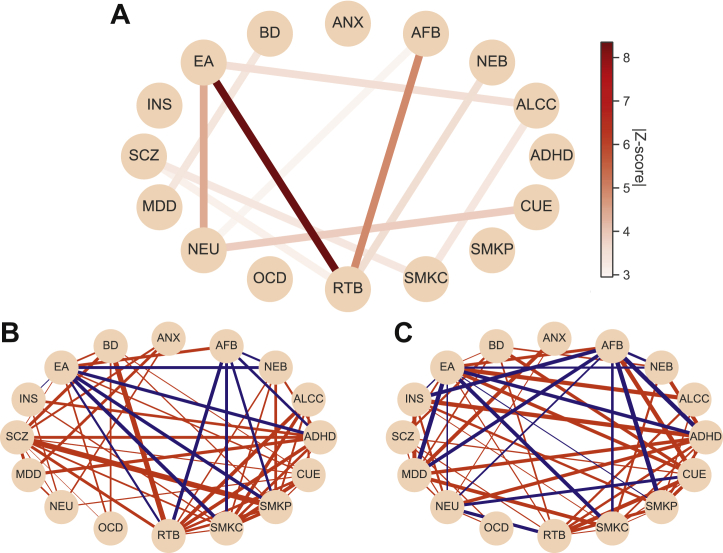
Figure 3.
(A) Network plot showing between-trait genetic correlations with a significant sex difference as computed by z score. The edge color represents the absolute value of the z score for the difference in genetic correlation between the same 2 phenotypes in females vs. males. Only pairs of traits with false discovery rate corrected q < .05 sex difference are shown. (B, C) Between-trait, within-sex genetic correlation analysis. Network plots for genetic correlation estimates (rg) for pairs of traits in (B) males and (C) females, where each node represents a trait, and the edge represents positive (red) or negative (blue) genetic correlation. The thickness of the edge represents −log10(q value) of correlation significance. Only genetic correlations with false discovery rate corrected q < .05 are shown. Genetic correlations were visualized using the Python package Networkx (50) and Matplotlib (51). ADHD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; AFB, age at first birth; ALCC, alcohol use; ANX, anxiety disorders; ASD, autism spectrum disorder; BD, bipolar disorder; CUE, cannabis use (ever); EA, educational attainment; INS, insomnia; MDD, major depressive disorder; NEB, number of children ever born; NEU, neuroticism; OCD, obsessive-compulsive disorder; RTB, risk-taking behavior; SCZ, schizophrenia; SMKC, smoking (current); SMKP, smoking (previous).