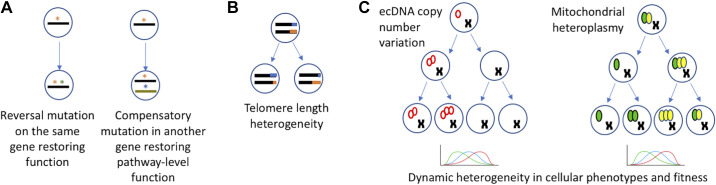
Figure 2.
Genetic drivers of dynamic heterogeneity in tumors. A: reversal mutations during tumor progression restore cancer gene function or compensate for gain- or loss-of-function at the pathway-level. *Genetic alterations on the same gene or on different genes. B: dynamic changes in telomerase expression and telomere length heterogeneity with implications for genomic instability during cancer progression. Different colors (blue and orange) display telomeres of different lengths. C: examples of genetic drivers of dynamic heterogeneity in cancer by copy number variation. Red empty ovals represent extrachromosomal circular DNA (left), and green and yellow filled ovals represent varied proportion of mutated and wild-type mitochondrial DNA (right). Replication and asymmetric distributions can lead to skewed distributions, and dynamic heterogeneity in tumors.