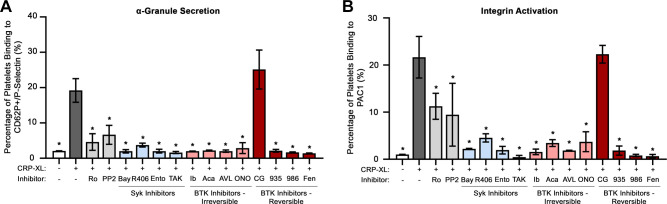
Figure 3.
Effects of Syk and BTK inhibitors on platelet α-granule secretion (A) and integrin activation (B). Replicate samples (n = 3) of washed human platelets (2 × 108/mL) were treated with the selected Syk and BTK inhibitors or with vehicle (0.1% DMSO), stimulated with CRP-XL (10 µg/mL), and stained with APC-CD62P and FITC-PAC1 to monitor for platelet surface expression of P-selectin and integrin activation, respectively, using flow cytometry. Thresholds for platelet surface integrin and P-selectin expression were set based on the negative control (−CRP-XL/−inhibitor), such that percentage of expression is 0.5%. Representative FACS traces are depicted in Supplemental Fig. S2. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA test and a Dunnett’s multiple comparison test on GraphPad PRISM. Statistical significance is indicated by one asterisk (*) for a P value < 0.001. AVL, AVL-292 (spebrutinib); Bay, Bay 61-3606; BTK, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; CG, CG-806; Fen, fenebrutinib; ONO, ONO-4059 (tirabrutinib); R406, fostamatinib; Syk, spleen tyrosine kinase; 935, BMS-935177; 986, BMS-986195; Ento, entospletinib; Ib, ibrutinib; TAK, TAK-659; Ro, Ro 31-8220; Aca, acalabrutinib; CRP-XL, cross-linked collagen-related peptide.