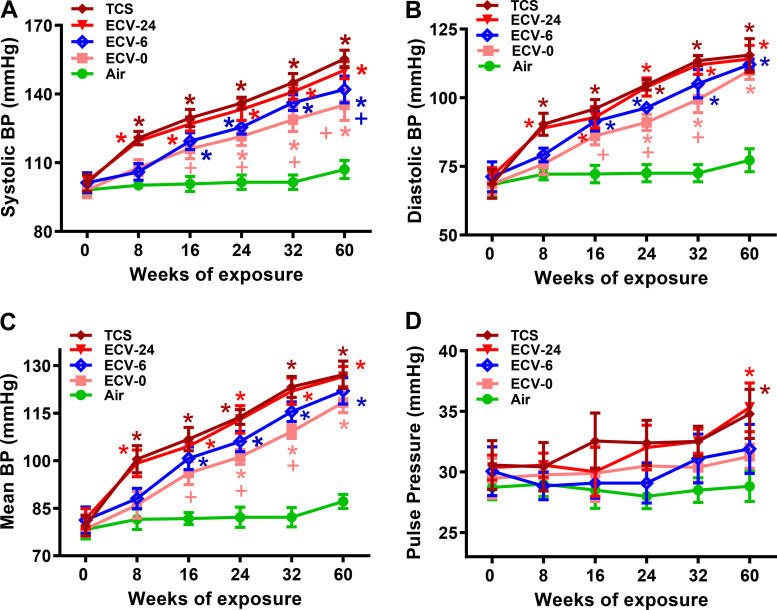
Figure 4.
Effect of e-cigarette vape (ECV) or tobacco cigarette smoking (TCS) exposure on blood pressure. Systolic BP (SBP; A), diastolic BP (DBP; B), mean BP (MBP; C), and pulse pressure (PP; D) in mice exposed to ECV and TCS at 16, 24, 32, and 60 wk. Data are expressed as means ± SE of 10 independent measurements in each group at each exposure time. TCS and ECV exposures increased SBP, DBP, and MBP as a function of the durations of exposure. Significant elevations in PP were seen in ECV-24 and TCS groups at 60 wk compared with air-exposed mice but not in ECV-0 and ECV-6 groups. ECV-0, ECV with 0 mg/mL NIC; ECV-6, 6 mg/mL NIC; ECV-24, 24 mg/mL NIC; NIC, nicotine. *Significant difference from air-exposed control at P < 0.05; +significant difference from TCS-exposed group at P < 0.05.