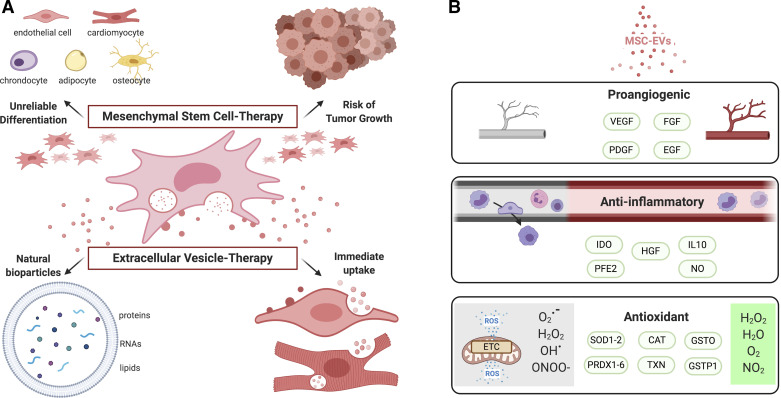
Figure 1.
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)- and extracellular vesicle (EV)-based therapies. A: stem cell-based treatments in models of myocardial infarction have led to short-lasting clinical improvements with unreliable or less defined differentiation and risk of tumor growth, contrary to immediate and natural paracrine effects that EV contents may provide. B: MSC-EVs have been shown to have proangiogenic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties that result in cardioprotection. CAT, catalase; EGF, epidermal growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; GSTO, glutathione S-transferase O; GSTP1, glutathione S-transferase P1; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IDO, indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase; IL-10, interleukin 10; NO, nitric oxide; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PFE2, prostaglandin E2; PRDX1-6, peroxiredoxin 1-6; SOD1-2, superoxide 1-2; TXN, thioredoxin; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor. Created with BioRender.com and published with permission.