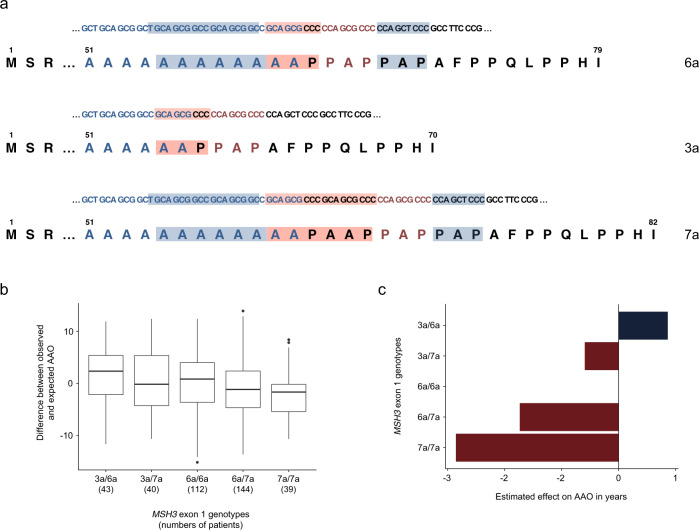
Fig. 3. The length polymorphism in exon 1 of MSH3 and its correlation within different genotypes with age at onset (AAO) in X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (XDP) patients.
a cDNA and amino-acid sequences showing the wild-type sequence, the shortest (c.162_179del;199_207del), and the longest (c.181_189dup) allele of MSH3 exon 1, i.e., 6a, 3a, and 7a alleles, respectively. The sequences are based on the MSH3 transcript ID ENST00000265081.7 (https://www.ensembl.org). Blue shading highlights the region deleted in the shortest allele (stretch of six alanines (A) and three other amino acids (proline, alanine, proline—PAP)). Red shading indicates the region duplicated in the longest allele. M: methionine (start codon); S: serine, R: arginine, AFPPQLPPHI: amino-acid sequence from the length polymorphism to the end of MSH3 exon 1. b Difference between the observed and predicted (based on the hexanucleotide repeat number) AAO negatively correlates with the number of 7a alleles in a genotype. Box-plot elements: center line: median; box limits: upper and lower quartiles; whiskers: 1.5× interquartile range; points: outliers. c Disease onset is delayed by ~4 years in heterozygous carriers of the shortest allele (3a/6a) in comparison to the patients homozygous for the longest MSH3 allele (7a/7a). Red color designates a harmful effect (earlier AAO), while blue depicts a protective effect (later AAO). The effect estimates are based on the linear regression model. Source data are provided as a Source data file.