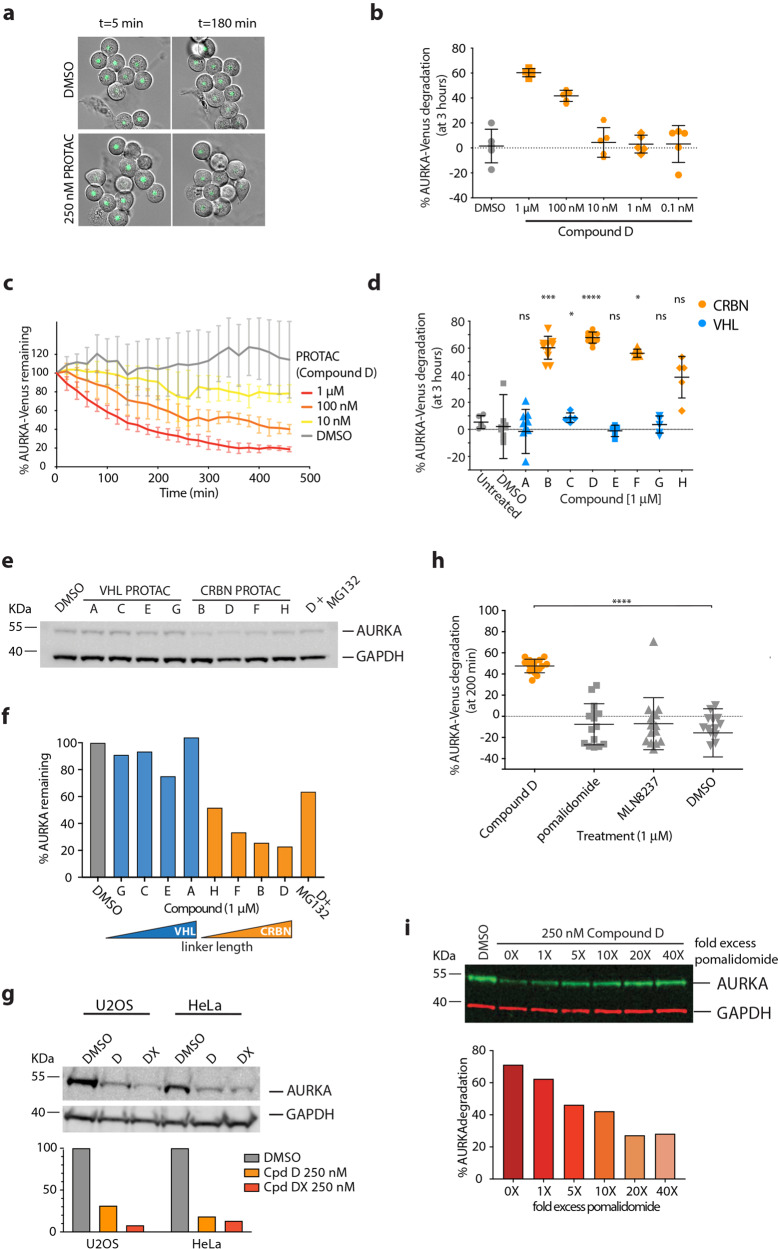
Fig. 1. AURKA destruction following treatment with CUL4-based PROTACs.
a–d AURKA-VenusKI degradation in STLC-arrested RPE-1 cells, measured by quantitative timelapse imaging. a Examples of fields of cells treated with a PROTAC (Compound D) or vehicle control (DMSO). Venus fluorescence was measured in individual cells and plotted as an end-point assay (percentage of AURKA-VenusKI degradation after 3 h) (b) or as percentage of AURKA-VenusKI remaining over time (to show the kinetics of degradation) (c). b Scatter plots showing response to different doses of PROTAC (Compound D) or DMSO, with whiskers indicating mean ± SDs. c Time-course of AURKA-VenusKI degradation plotted as mean fluorescence ± SDs at each time point (n ≥ 7 cells). d Comparison of percentage degradation of AURKA-VenusKI after treatment with potential PROTAC compounds directed to CUL4A (via CRBN) or CUL2 (VHL) ubiquitin ligases (listed in Table 1). Scatter plots show pooled results from two separate experimental repeats with whiskers indicating mean values and SDs. Results of Kruskal–Wallis multiple ANOVA, and the Dunn’s post-hoc multiple comparison test to DMSO are indicated. e, f Degradation of endogenous AURKA in HeLa cells following 3 h treatment with PROTACs, with or without 42 µM proteasome inhibitor MG132, measured by quantitative immunoblotting (e) to plot percentage protein remaining, ordered to show increasing linker size across the series (f). g U2OS and HeLa cells were treated for 3 h with 250 nM Compound D (PROTAC-D) or a new compound with increased linker length (PROTAC-DX). Endogenous AURKA levels were measured by immunoblot and plotted as percentage remaining compared to DMSO treatment after normalization to GAPDH loading control. The experiment shown is one of two repeats that gave identical results. h Degradation of AURKA-VenusKI was measured in prometaphase cells treated with 1 μM PROTAC-D, MLN8237, or pomalidomide. Kruskal–Wallis multiple ANOVA, and the Dunn’s post-hoc multiple comparison test to DMSO, showed that only PROTAC-D caused significant AURKA-Venus degradation. i Degradation of endogenous AURKA was quantified by immunoblot from mitotic-enriched U2OS cells treated with 250 nM PROTAC D in the presence of 1–40-fold molar excess of pomalidomide. Data representative of two experiments (the other in HeLa cells). Only cells that did not exit mitosis during filming (scored as onset of cortical contractility followed by respreading) were included in the analyses shown in Fig. 1a–d, h).