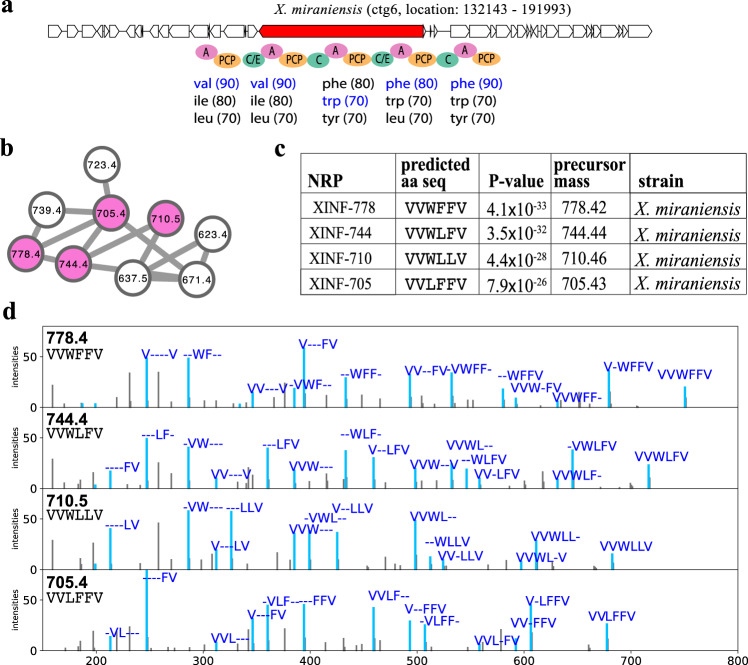
Fig. 4. Identifying xenoinformycin (XINF) NRP family.
a The BGC generating the NRP in X. miraniensis along with NRPS genes (shown in red) and the A-, C-, PCP-, and C/E-domains appearing on the corresponding NRPS. The rest of the genes in the corresponding contigs are shown in white. Three highest-scoring amino acids for each A-domain in this BGC (according to NRPSpredictor2 (ref. 15) predictions) are shown below the corresponding A-domains. Amino acids appearing in the NRP VVWFF identified by NRPminer (with the lowest p value) are shown in blue. b Spectral network formed by the spectra that originate from NRPs in the xenoinformycin family. A node is colored if the corresponding spectrum forms a statistically significant PSM (with p value threshold 10−15) and not colored otherwise. c Sequences of the identified NRPs in the xenoinformycin family (with the lowest p value among all spectra originating from the same NRP). XINF represents xenoinformycin. The p values are computed based on MCMC approach using MS-DPR89 with 10,000 simulations. d For each identified NRP, an annotated spectrum forming a PSM with the lowest p value is shown.