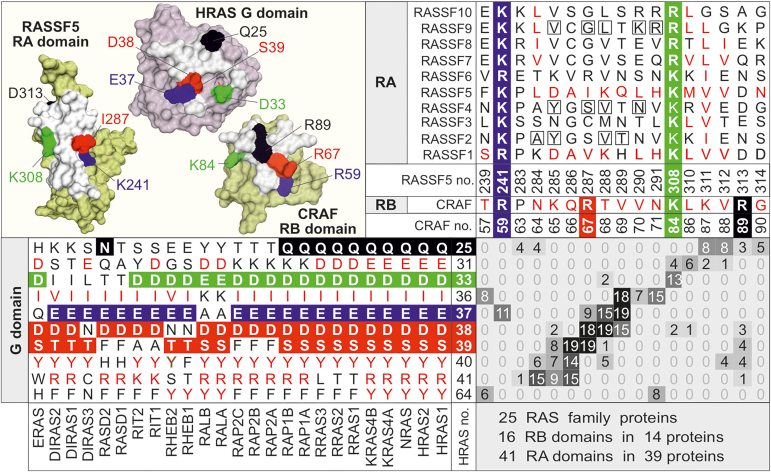
Figure 3.
Interaction matrix adapted for the structures of RAS complexes with effector domains. Interaction matrix of RAS family proteins with the RA/RB proteins used in this study is generated to demonstrate interacting residues in respective structures (see Table S6). It comprises the amino acid sequence alignments of the RAS proteins (lower left panel) and the effector domains (upper right panel), respectively, extracted from the complete alignments in Figs. S2–S4. Each element corresponds to a possible interaction of RAS residues (row; HRAS numbering) and effector (column; CRAF and RASSF5 numbering, respectively). The number of actual contact sites between RAS and the effector domains (with distances of 4 Å or less) were calculated and are indicated with positive numbers for matrix elements. Extracted structures of HRAS (in orchid) and the RA domain of RASSF5 and RB domain of CRAF (in olive) from their surface complexes are presented (top left panel). Key interaction hotspots with the same color codes are highlighted on the surface structures as well as in the interaction matrix and the secondary structures, respectively. Boxed residues in RASSF2, 4, and 9 were replaces to RASSF1 and 5, respectively, to validate the impact of these hotspot residues on the interaction with RAS family proteins (Fig. 4).