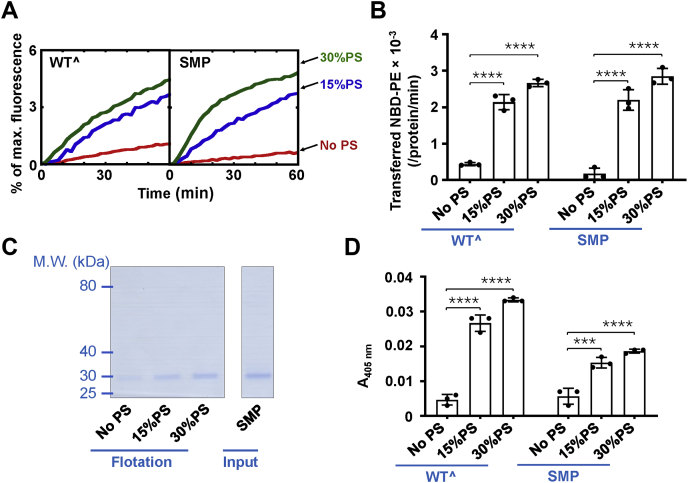
Figure 6.
The SMP domain of Tcb3 interacts with PS to transfer lipids between membranes.A, effect of PS on the lipid transfer activity mediated by Tcb3 or the SMP domain. Lipid transfer of the protein-free liposomes in the presence of 1 μM Tcb3 (WTˆ or the SMP domain). PS was reconstituted into the liposomes at the indicated concentrations. The lipid transfer reactions included 0.1 mM EGTA. B, initial lipid transfer rates of NBD-labeled phosphatidylethanolamine in the reactions shown in A. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent replicates). p Values were calculated using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. F (2, 12) = 290.2, p < 0.0001 for lipid factor and F (1, 12) = 0.005379, p = 0.9427 for protein factor. The interaction between the two factors is F (2, 12) = 2.350, p = 0.1376. C, Left, Coomassie blue–stained SDS-PAGE gel showing the binding of the SMP domain to protein-free liposomes in the presence of 0.1 mM EGTA. The liposomes were prepared with phosphatidylcholine and the indicated percentage of PS. Right, Coomassie blue–stained gel showing the recombinant Tcb3 SMP domain protein. The amount of protein was loaded as 30% of the total input. D, effect of PS on the membrane tethering activity of Tcb3. The turbidity of the protein-free liposomes with the indicated percentage of PS in the presence of 1 μM Tcb3 (WTˆ or the SMP domain) was shown. The reactions included 0.1 mM EGTA. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent replicates). p Values were calculated using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ∗∗∗p = 0.0001. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. F (2, 12) = 266.1, p < 0.0001 for lipid factor and F (1, 12) = 117.2, p < 0.0001 for protein factor. A significant interaction between the two factors is F (2, 12) = 38.31, p < 0.0001. PS, phosphatidylserine.