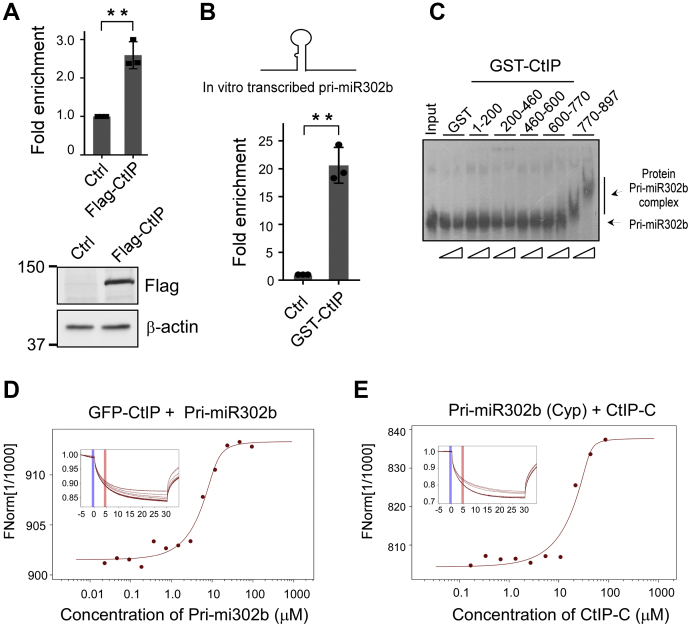
Figure 4.
CtIP binds to pri-miRNA via Sae2-like domain.A, anti-Flag RNA-ChIP was performed in HCT116 cells expressing Flag-CtIP or empty vector using pri-miR302 primer sets. The ChIP value in the control was set as 1 for normalization. Data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. The p value is indicated as ∗∗p < 0.01. B, in vitro–transcribed pri-miR302b was mixed with bead-immobilized GST-CtIP full-length protein. RNA was eluted from beads and subjected to quantitative RT-PCR analysis using pri-miR302b primer sets. Data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. The p value is indicated as ∗∗p < 0.01. C, electrophoretic mobility shift assay was performed with GST alone or indicated GST-CtIP variants using an in vitro–transcribed 32P-labeled pri-miR302b probe. The band shifts resulting from specific binding to the CtIP variant are shown. D and E, microscale thermophoresis analysis showing pri-miR302b interacted with CtIP in vitro. Titration of cell lysates containing pri-miR302b in vitro–transcribed to a constant amount of GFP-CtIP or purified CtIP-C protein to Cyp-labeled pri-miR302b induced a pronounced microscale thermophoresis signal change and yielded Kd = 3.94 μM (D) and Kd = 2.39 μM (E), respectively. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; CtIP, C-terminal-binding protein–interacting protein; GST, glutathione-S-transferase; HCT116, human colon cancer cell line; pri-miRNA, miRNA primary transcripts.