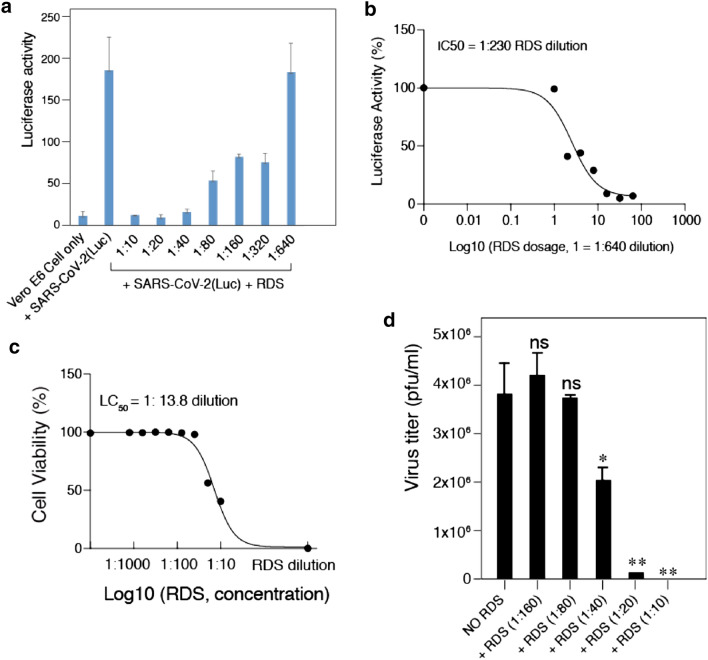
Fig. 3.
RDS dosage-dependent inhibition of SARS-CoV-2(Luc) pseudovirus and wild-type SARS-CoV-2. A and B Vero E6 cells were pretreated with serially diluted RDS, and infected with SARS-CoV-2(Luc) pseudovirus. Cells were washed to remove the virus and RDS, and cultured in the absence of RDS. Inhibition of viral infection was quantified at 72 h post infection by luciferase assay. Uninfected cell and SARS-CoV-2-Luc-infected but RDS-untreated cells were used as controls. The assay was performed in triplicate. The dose–response curve was plotted, and the IC50 of RDS was quantified to be at 1:230 dilution. C The cytotoxicity of RDS on Vero E6 cells was also quantified using propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. Cells were treated with serially diluted RDS for 4 h, washed to remove RDS, and cultured in the absence of RDS for 72 h. The dose–response cytotoxicity curve was plotted, and the LC50 of RDS was calculated to be at 1:13.8 dilution. D RDS inhibits infectious SARS-CoV-2 infection. Vero E6 cells were pretreated with serially diluted RDS, and infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the presence of RDS. Inhibition of viral replication was quantified by plaque assays of the virus released at 48 h post infection. Inhibition assays were performed in triplicate, and statistical significance was determined using One-Way ANOVA with Dunnett’s Post Test in Prism 7 (Graph Pad). Significance values are indicated using asterisks as follows; *p < 0.02, **p < 0.01. The designation “ns” stands for “not significant”