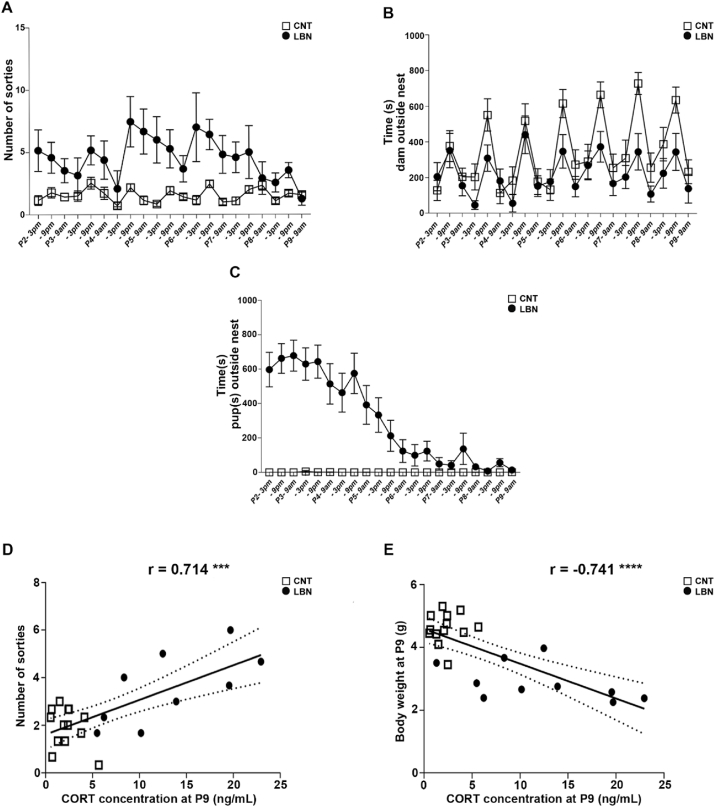
Fig. 2.
Heterogeneity in the LBN enables stratification based on the offspring's CORT response: importance of maternal fragmentation. (A) LBN litters showed an increase in the number of sorties from the nest compared to control (CNT) dams Mixed-effects model, for the stress effect: F(1,26) = 47.17, p < 0.0001, n = 14 CNT and n = 14 LBN litters. (B) LBN dams spend more time inside the nest compared to CNT dams. Mixed-effects model, for the stress effect: F(1,26) = 17.39, p = 0.0003; for time: F(8.712, 193.8) = 7.260, p < 0.0001, n = 14 CNT and n = 14 LBN litters. (C) LBN pups spent more time outside the nest compared to CNT pups. Mixed-effects model, for the stress effect: F(1,26) = 87.42, p < 0.0001; for time: F(6.028, 134.1) = 11.03, p < 0.0001, for interaction time x stress: F(20, 445) = 10.97, p < 0.0001, n = 14 CNT and n = 14 LBN litters. (D) Dam sorties at P3 correlated positively with CORT level of the litter at P9, Pearson r = 0.714, p = 0.0002, n = 22 litters. (E) The decrease in the body weight correlated negatively with the increase in the CORT level at P9, Pearson r = -0.741, p < 0.0001 n = 23 litters. ***p < 0.001 ****p < 0.0001.