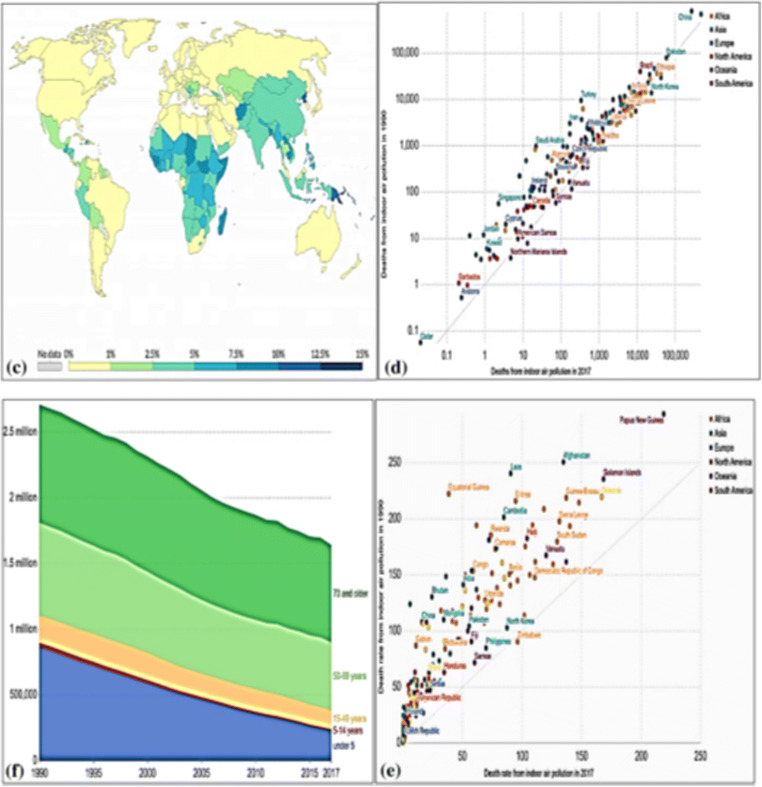
Fig. 2.
c Death mediated by indoor and outdoor air pollution worldwide. An air pollution color intensity illustrating the global death rate produced by indoor air pollution. The percentage displays the rate of death due to indoor air pollution in comparison to other diseases. d The number of indoor air pollution deaths in 1990 compared to 2017. e Death from indoor air pollution age-dependent. Older people over 69 are at greater risk for indoor air pollution. f Rate of indoor air pollution per 100,000 people in 1990 compared to 2017 country distribution. Increasing indoor air pollution is a global concern (Source Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation 2020 under creative common license attribution). Panels c, d, f, and e were reused from Fig. 3 of Paital B, Agrawal PK. Air pollution by NO2 and PM2.5 explains COVID-19 infection severity by overexpression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in respiratory cells: a review. Environ Chem Lett. 2020 Sep 18:1-18. doi: 10.1007/s10311-020-01091-w obtained with License Number 4971970782195