Fig. 1.
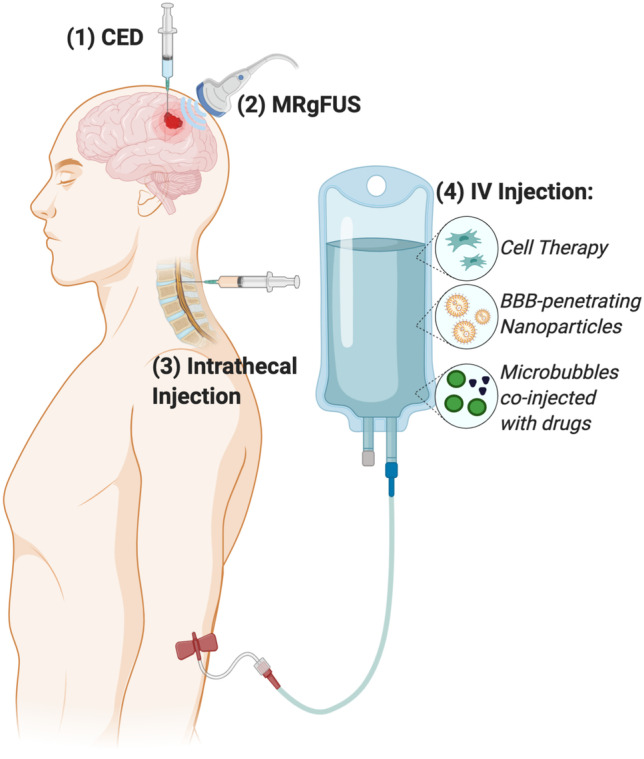
Routes of administration for therapeutic delivery to intracranial GBM. Routes of administration enabling drug delivery across the BBB to the tumor site include (1) direct intratumoral injection or convection enhanced delivery (CED); (2) MRI-guided focused ultrasound to cause transient disruptions in the BBB (MRgFUS); (3) intrathecal injection into the CSF; and (4) intravenous (IV) injection of tumor-homing cell therapies, nanocarriers conjugated with BBB-penetrating ligands, or microbubbles designed to cavitate upon MRgFUS application and allow co-injected drugs to cross the BBB
