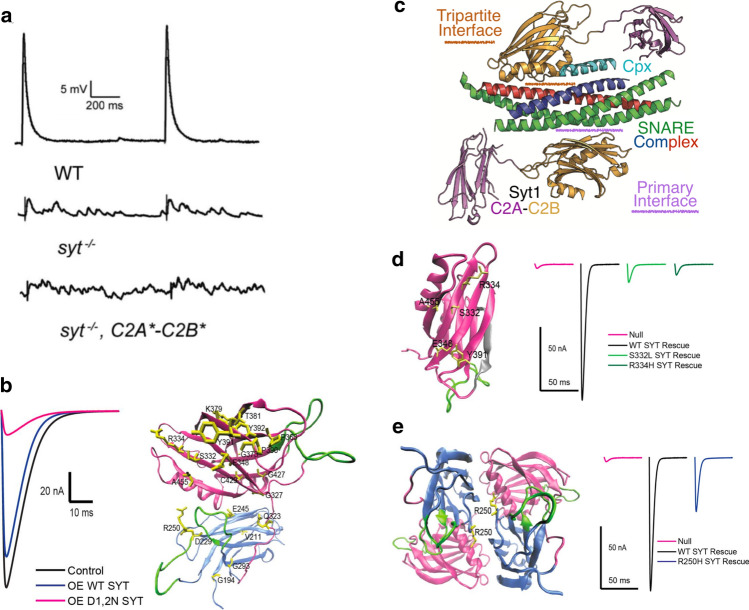
Fig. 4.
Function of SYT1 in SV fusion. a Syt1 null mutants reduce synchronous fusion and enhance asynchronous release and mini frequency. Rescue with a Syt1 transgene with defective Ca2+ binding to C2A(*) and C2B(*) fails to support synchronous fusion and causes higher rates of spontaneous release. b Overexpression of a C2B Ca2+ binding mutant (D1,2N) suppresses release compared to overexpression of wildtype SYT1. Twenty essential residues mapping to C2A (blue) or C2B (magenta) were identified in an intragenic suppressor screen that blocked the dominant-negative effects. c. Structure of the primary and tripartite interface of the SYT1/SNARE/CPX complex. d Location of mutations disrupting the primary SNARE interface on the SYT1 C2B domain. The polybasic stretch is shown in grey and localizes to the opposite C2B surface. SNARE-binding mutations fail to rescue release defects in Syt1 null mutants (right panel). e Location of the R250H mutation at the SYT1 dimer interface that disrupts oligomerization. This mutation reduces SV release (right panel), though not as severely as SNARE-binding mutants. a Modified from [49], b, d, and e modified from [62], and c modified from [38]