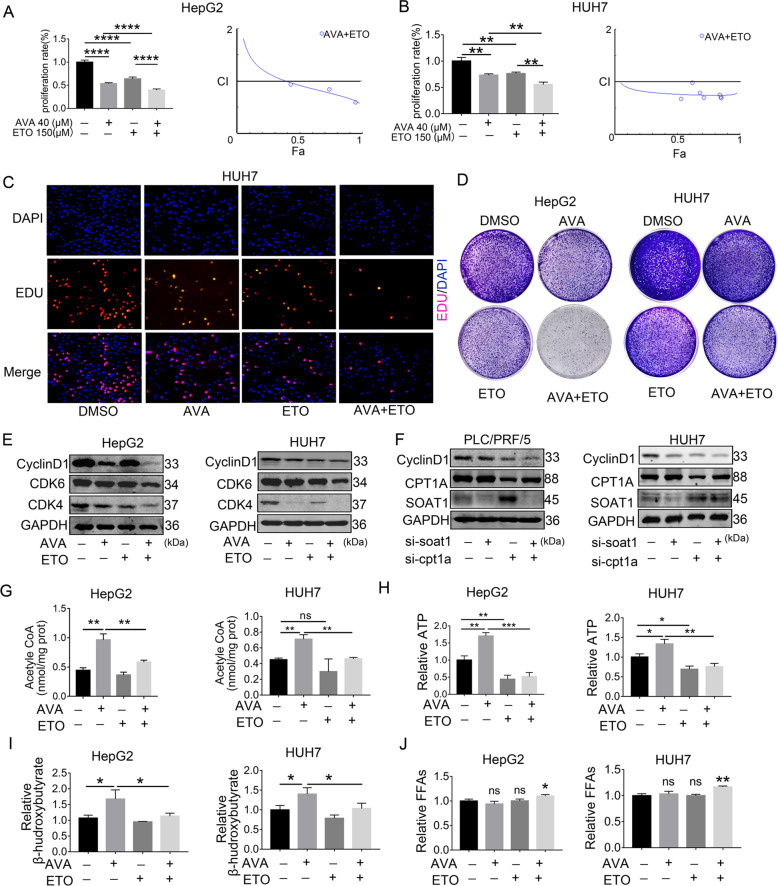
Fig. 7. Combined avasimibe and etomoxir enhance the efficacy by disrupting lipid homeostasis in HCC in vitro.
A–B CCK8 assay showed that combined avasimibe and etomoxir enhanced the efficacy in the HepG2 and HUH7 (means ± SEM, n = 3). Chou and Talalay analyzed the combination indices (CI) of combined AVA and ETO for 48 h in HepG2 and HUH7. The straight line at CI = 1 represents the additive effects of both drugs. Fraction effect (FA): growth inhibition rate. C Representative images of the EdU staining assay in HUH7 cells treated with AVA, ETO, or both. D The colony formation assay of HepG2 and HUH7 cells cultured with 2 μM AVA and/or 25 μM ETO for 14 days. E Western blot analysis of CDK4, CDK6, and Cyclin D1 in HepG2 and HUH7 cells treated with 20 μM AVA and/or 150 μM ETO. F Western blot analysis of CyclinD1, CPT1A, and SOAT1 after transfection with si-SOAT1and/or si-CPT1A in PLC/PCF/5 and HUH7. G–I Levels of total acetyl-CoA, ATP and β-hydroxybutyrate in HCC cells treated with AVA (5 μM) and/or ETO (50 μM) (mean ± SEM, n = 3); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ns: no significance. J Levels of intrahepatic FFAs in HepG2 and HUH7 treated with AVA (5 μM) and/or ETO (50 μM) (mean ± SEM, n = 3); *p < 0.05.