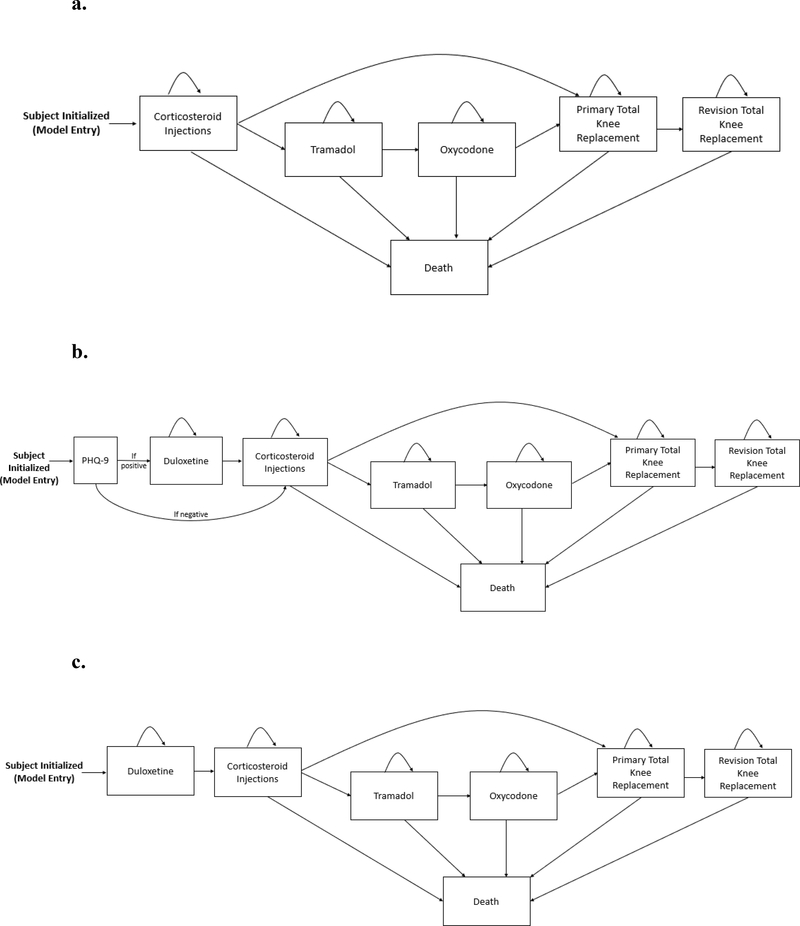
Figure 1.
Panel A. The usual care (UC) treatment sequence for knee OA in the OAPol Model. Subjects are initialized based on specific cohort characteristics and progress through the regimens outlined, including corticosteroids, tramadol, oxycodone (for some subjects, others skip opioid regimens), total knee replacement, and revision total knee replacement. Subjects remain on each treatment until it is no longer effective. Death can occur at any point in the sequence.
Panel B. The depression screening treatment sequence for knee OA in the OAPol Model. Subjects are initialized based on specific cohort characteristics and are screened for depression using the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9) at initialization. If they screen positive, they receive duloxetine before UC, consisting of corticosteroids, tramadol, oxycodone (for some subjects, others skip opioid regimens), total knee replacement, and revision total knee replacement. If they screen negative, they proceed directly to UC. Subjects remain on each treatment until it is no longer effective. Death can occur at any point in the sequence.
Panel C. The universal duloxetine treatment sequence for knee OA in the OAPol model. Subjects are initialized based on specific cohort characteristics and receive duloxetine before progressing through the rest of the UC treatments, including corticosteroids, tramadol, oxycodone (for some subjects, others skip opioid regimens), total knee replacement, and revision total knee replacement. Subjects remain on each treatment until it is no longer effective. Death can occur at any point in the sequence.