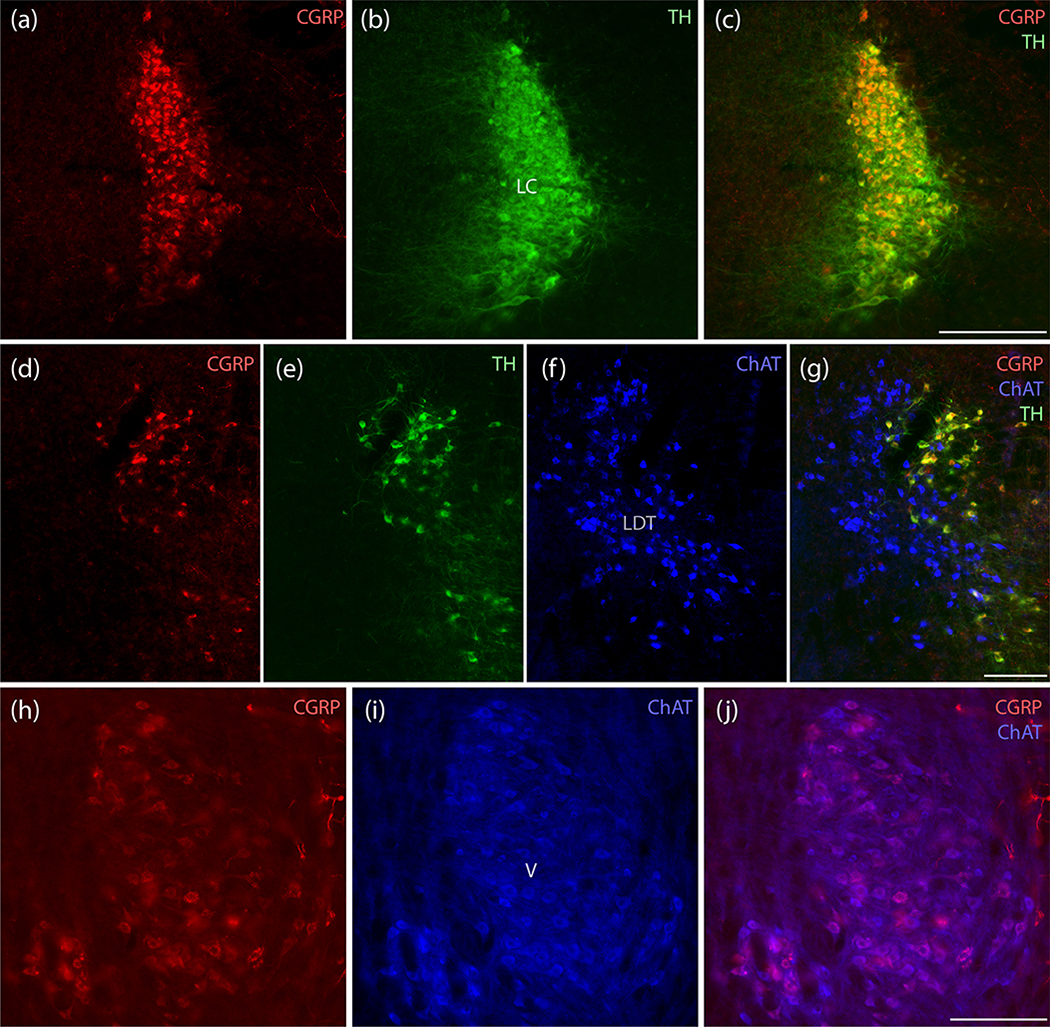
Figure 5.
CGRP neurons in the LC are catecholaminergic, while those in V are cholinergic. (a–c) All LC neurons containing CGRP immunofluorescence (red) also contain tyrosine hydroxylase (TH, green). All LC neurons appear to contain CGRP, but labeling intensity is greater dorsally. (d–g) Rostrally in this region, CGRP-immunofluorescence is mutually exclusive with cholinergic neurons in the lateral dorsal tegmental nucleus (LDT), which are immunoreactive for choline acetyl transferase (ChAT, blue), and again co-localizes with TH in rostral LC neurons. (h–j) In contrast, the prominent CGRP immunofluorescence in a subset of trigeminal motor neurons uniformly co-localizes with ChAT immunoreactivity (blue). Scale bars are 200 μm (a–c), 200 μm (d–g), and 200 μm (h–j).