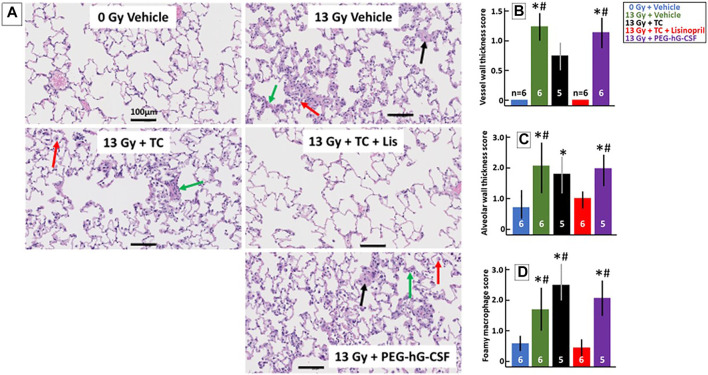
FIGURE 6.
Lisinopril mitigates histological lung injury after 13 Gy leg-out PBI. Representative histological sections of lung tissue harvested at 56-days after 13 Gy leg-out PBI were stained with H&E for each treatment group (A). Irradiated rats given the vehicle or PEG-hG-CSF showed increased alveolar wall thickness cellularity (green arrow), increased vessel wall thickness (black arrow) and foamy macrophages (red arrow). Black bars represent 100 μm. Graphical representations of the H&E-stained lung sections are shown for vessel wall thickness (B), alveolar wall thickness (C) and foamy macrophages (D). Vessel wall thickness (B) were increased in irradiated rats given the vehicle or PEG-hG-CSF, whereas TC + lisinopril mitigated lung injury (p < 0.05, denoted by * compared to controls and # compared to TC + lisinopril). Irradiation increased alveolar wall thickness (C) in all irradiated groups compared to control (p < 0.05, denoted by *) except for the TC + lisinopril group. Alveolar wall thickness was also increased compared to the TC + lisinopril group in the irradiated vehicle and PEG-hG-CSF groups (p < 0.05, denoted by #). Foamy macrophages (D) were significantly increased in irradiated rats given the vehicle, TC or PEG-hG-CSF (p < 0.05, denoted by * compared to controls and # compared to TC + lisinopril). Numbers in the bars represent N in each group and bars are means with standard deviations.