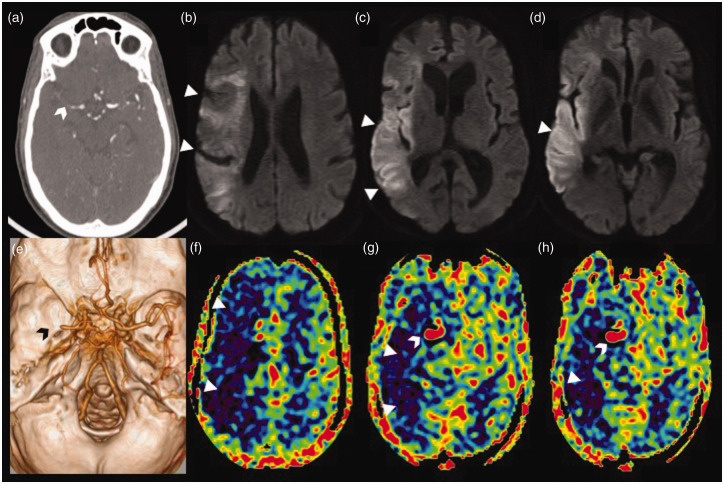
Figure 6.
Stagnation of arterial spin labelling (ASL) signal due to distal occlusion in an acute right middle cerebral artery (MCA) stroke. Axial computed tomographic angiogram image (a) showing cut-off of the proximal M1 segment of the right MCA with faint contrast opacification of the distal M1 MCA (white arrowhead). Volume rendered angiographic image (e) showing the right M1 MCA cut-off (black arrowhead) with paucity of the cortical branches. Serial axial diffusion weighted images (b)–(d) showing areas of diffusion restriction (white triangles) in the cortical right MCA territory with relative sparing of the ganglio-capsular region. Serial axial ASL images at corresponding levels (f)–(h) showing a larger area of perfusion defect, seen as a low ASL signal (white triangles), with increased ASL signal (white arrowhead) within the communicating segment of the right internal carotid artery and the patent proximal right MCA stump due to stagnation of labelled spins (arterial transit artefact).