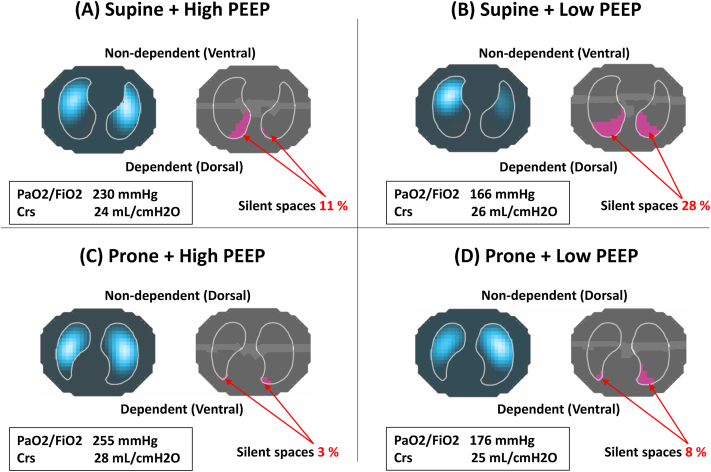
Fig. 1.
Respiratory variables, distribution of ventilation, and ‘silent spaces’ in Case 1
(A) High PEEP, Supine; (B) Low PEEP, Supine; (C) High PEEP, Prone; and (D) Low PEEP, Prone. In low PEEP
+
supine position, oxygenation was worst and the largest amount of ‘
silent spaces’
was observed, suggesting a massive lung collapse in dependent lung regions (B). High PEEP improved oxygenation, reduced the amount of ‘
silent spaces’
(A). Prone position by itself reduced the amount of silent spaces in dependent lung regions without increasing PEEP (D). The combination of high PEEP with prone position achieved highest oxygenation, least amount of ‘
silent spaces’
(C). PEEP =
positive end-expiratory pressure; Crs = respiratory system compliance.