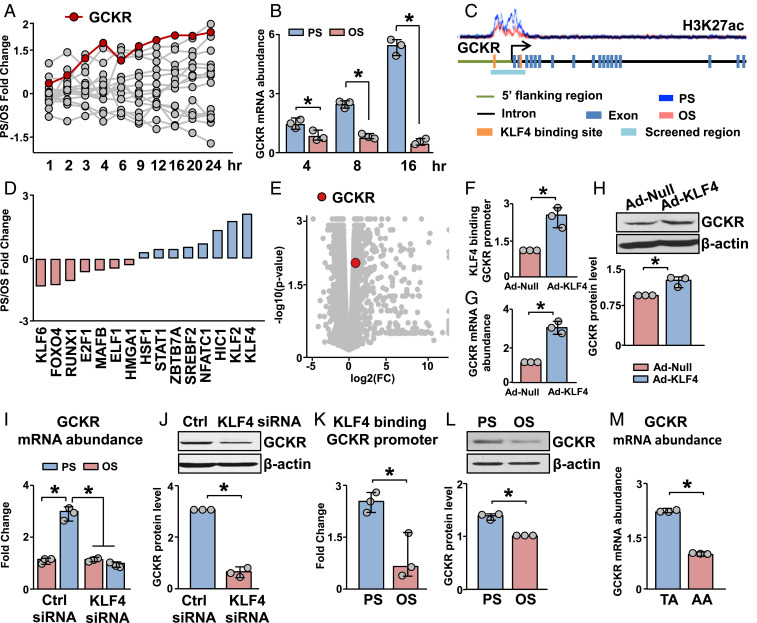
Fig. 2.
KLF4 regulates the expression of GCKR in response to PS. (A) Time course of PS/OS fold changes in mRNA level with a “glycolysis” gene ontology categorization in ECs exposed to PS or OS for 24 h. (B) qPCR analysis of GCKR mRNA expression in HUVECs subjected to PS or OS at 4, 8, and 16 h. (C) Level of H3K27ac in the GCKR promoter, which is annotated with the regions screened for TF binding sites. (D) RNA-seq data showing PS/OS fold change of TFs identified in the GCKR promoter as illustrated in C. (E) GCKR fold change and significance in RNA-seq data from HUVECs infected with Ad-null or Ad-KLF4 for 48 h. (F–H) HUVECs were infected with Ad-KLF4 for 48 h. Level of KLF4 binding to the GCKR promoter is shown in F, GCKR mRNA abundance in G, and GCKR protein abundance in H. (I) Levels of GCKR mRNA in HUVECs transfected with control (Ctrl) siRNA or KLF4 siRNA and subjected to PS or OS, respectively. (J) Levels of GCKR protein in HUVECs transfected with Ctrl siRNA or KLF4 siRNA and subjected to PS. (K and L) HUVECs were subjected to PS or OS. KLF4 binding to the GCKR promoter is shown in K and GCKR protein abundance in L. (M) GCKR mRNA abundance in the TA and AA from 7-wk-old C57BL/6 mice. *P < 0.05. Data are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.