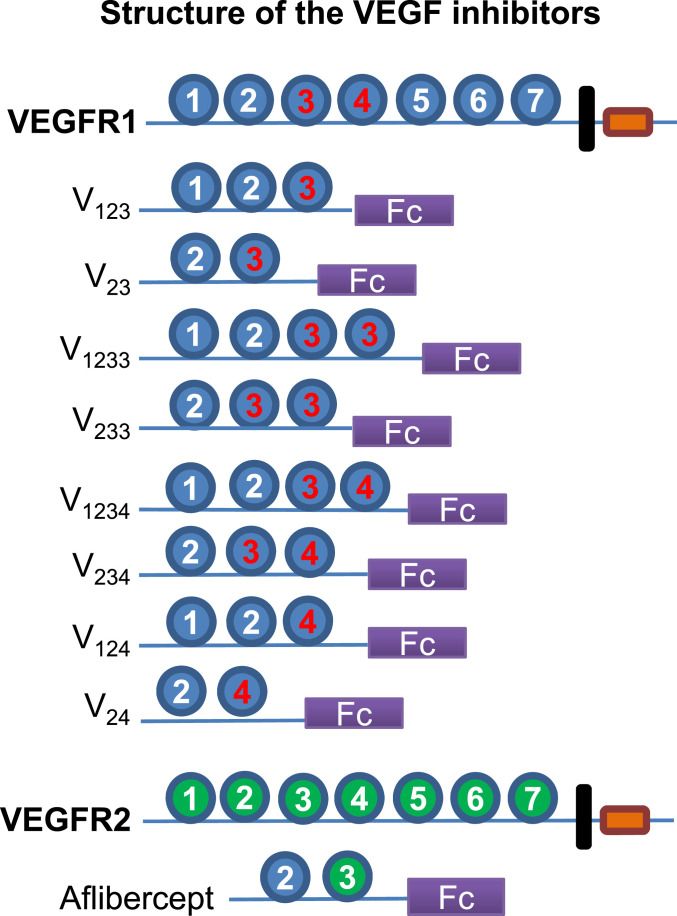
Fig. 1.
Immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain (D) organization of VEGFR1 and of the Fc fusion constructs designed in our study. Red label denotes heparin-binding domain. D2 is an indispensable binding element for VEGF and PlGF, responsible for ligand specificity (31). D3 plays an important role in binding affinity and stability (31, 32, 34). D3 of VEGFR1, but not D3 of VEGFR2, is a major heparin-binding site. V23 and aflibercept (Eylea) differ only in D3, which is from VEGFR2 in aflibercept. D4 is also a heparin-binding site, implicated in receptor dimerization and homotypic interactions (34). Each construct is shown as a monomer for simplicity, but the recombinant proteins are dimers due to the forced dimerization imposed by the Fc.