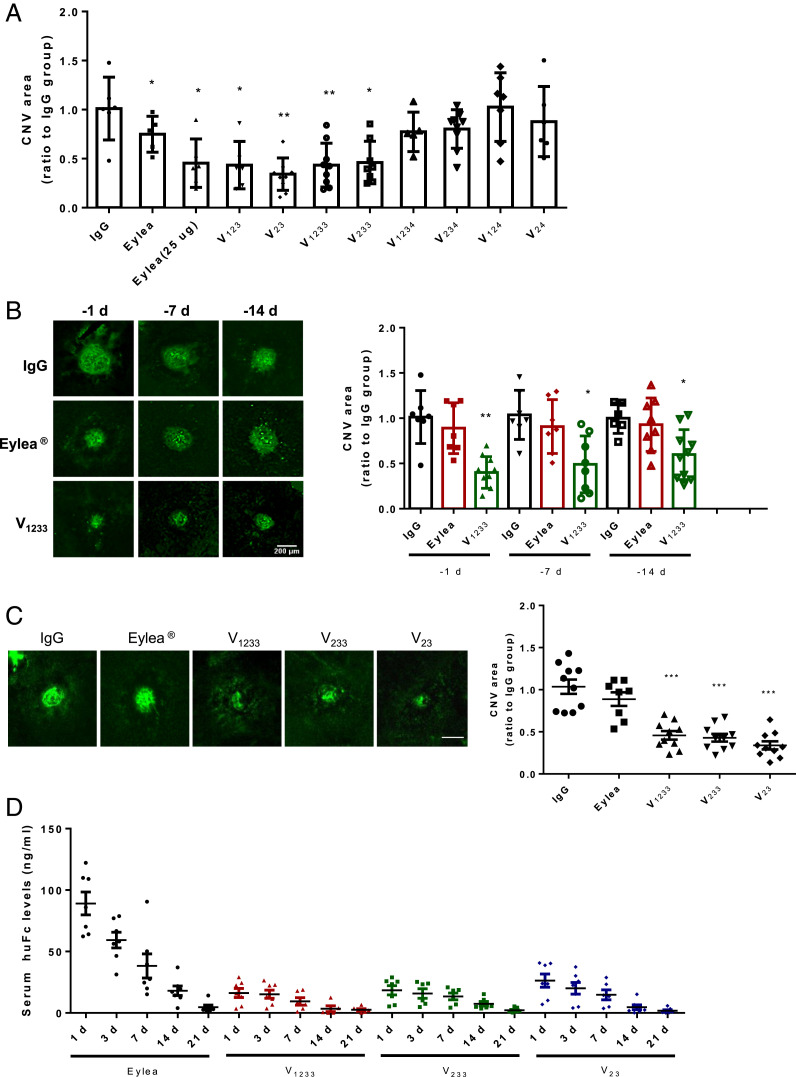
Fig. 5.
Effects of control IgG, Eylea, or VEGFR1 Fc fusion proteins on laser-induced CNV in adult mice. (A) Each protein was injected intravitreally in the mouse at the dose of 2.5 μg 1 d before laser treatment. Eylea was tested also at 25 μg. Asterisks denote significant differences (Student’s t test) compared to the appropriate IgG control groups (**P < 0.01, *P < 0.05). Data are based on three independent experiments with at least five mice per group. Note that the efficacy of Eylea is in line with the published literature in the same model. (B) Effect of the time of injection prior to injury on CNV area. Eylea at the dose of 2.5 μg had a significant reduction only when injected at day −1. In contrast, V1233 at the same dose significantly reduced CNV area even when injected 7 or 14 d prior to the injection. Left shows representative CD31 immunofluorescence images. Asterisks denote significant differences (Student’s t test) compared to the appropriate IgG control groups (**P < 0.01, *P < 0.05). n = 5. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. (C) V23, V233, and V1233, tested at equimolar doses (4.8 μg of Eylea and V23, 6.3 μg of V233, and 7.2 μg of V1233), show greater efficacy compared to Eylea. All agents were administered 14 d prior to the laser treatment. Seven days later, eyes were harvested, and data were analyzed. Asterisks denote significant differences (Student’s t test) compared to the appropriate IgG control groups (**P < 0.01, *P < 0.05). (D) Serum levels of Eylea, V23, V233, or V1233 in mice at different time points after intravitreal injection. Each molecule was injected in both eyes in equimolar amounts: 2.4 μg of Eylea and V23, 3.15 μg of V233, and 3.6 μg of V1233. After 1, 3, 7, 14, and 21 d, peripheral blood was collected from the tail vein. Human Fc levels were measured by ELISA. Values shown are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. n = 8 per point.