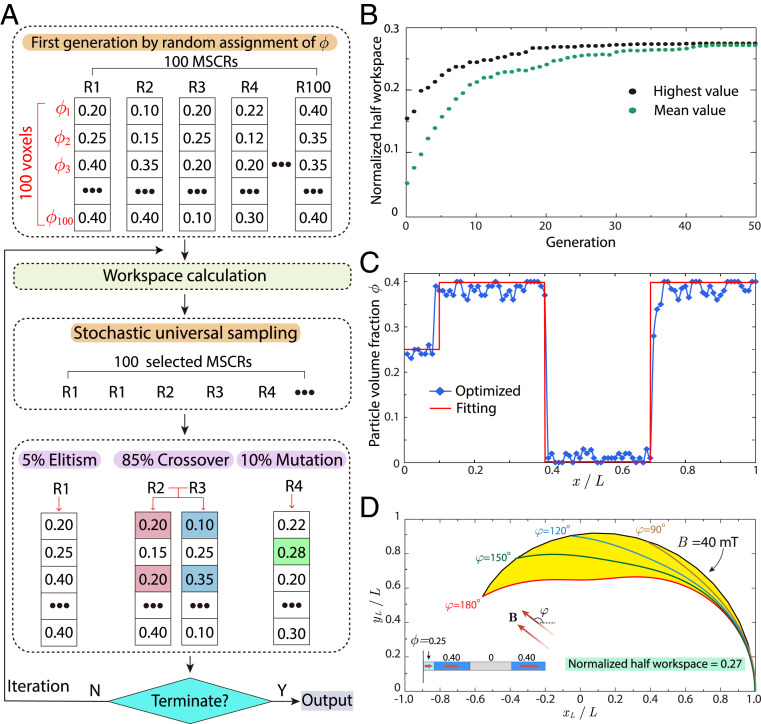
Fig. 4.
Design and optimization of MSCRs by the genetic algorithm. (A) The schematic flowchart of the optimization process. MSCRs with a larger workspace may be selected multiple times by stochastic universal sampling to reproduce the next generation via elitism, crossover, and mutation. (B) The highest and mean values of the normalized half workspaces of 100 MSCRs over generations. The normalized half workspaces of all MSCRs reach the maximum and optimal value, ∼0.27, after 40 generations. (C) The hard-magnetic particle distribution (blue marker) and its fitted function (red line) of the optimized MSCR at generation 40. (D) The normalized half workspaces of the optimized MSCR with the fitted magnetization and rigidity pattern (red line in C) is 0.27.