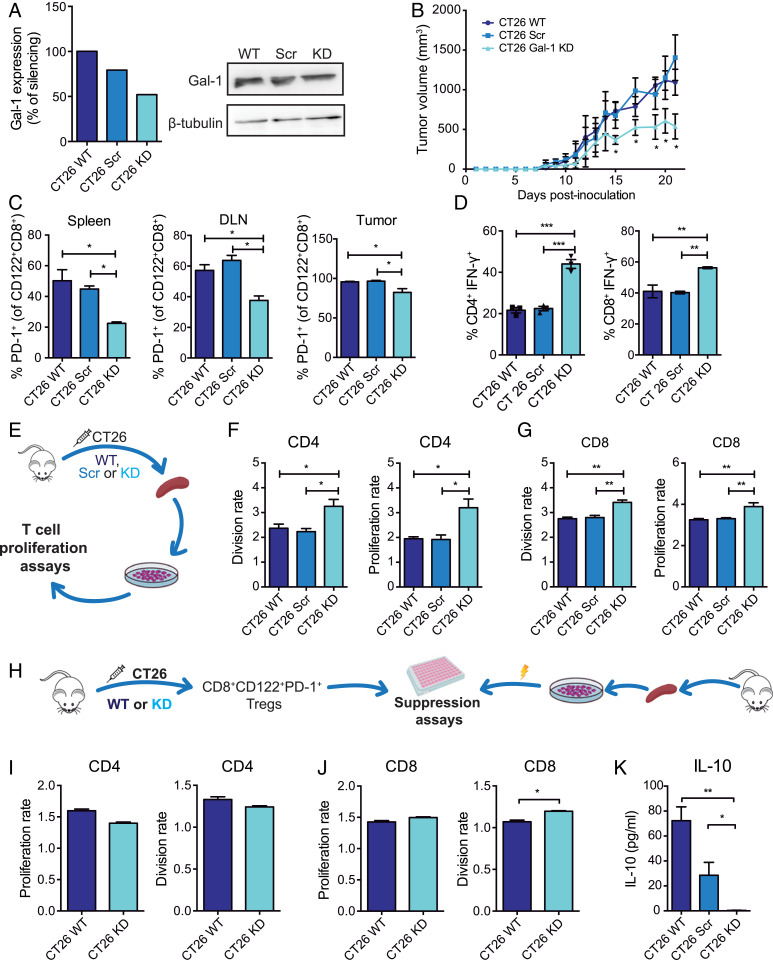
Fig. 3.
Tumor-derived Gal-1 increases the frequency of CD8+CD122+PD-1+ Tregs and accentuates their immunosuppressive capacity in the syngeneic CRC model. (A) Gal-1 expression detected by Western blot in CT26 WT cells stably transfected with shRNA (CT26 Scr) or with Gal-1–specific shRNA (CT26 Gal-1 KD). (B) Tumor growth kinetics in BALB/c mice subcutaneously inoculated with WT, Scr or Gal-1 KD CT26 cells. (C) Analysis of PD-1+ cells within the CD8+CD122+ T cell population isolated from the spleen, DLN, and tumors from mice inoculated with CT26 WT, Scr, or Gal-1 KD cells. (D) Flow cytometry analysis of intracytoplasmic IFN-γ in CD8+- and CD4+-activated T cells. (E) Schematic representation of proliferation assays performed with CFSE-labeled splenocytes. (F and G) Analysis of CD4+ and CD8+T cell proliferation and division index. (H) Schematic representation of suppression assays involving CD8+CD122+PD-1+ Tregs and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. (I and J) Proliferation and division index of CD4+ and CD8+ responder T cells. (K) Determination of IL-10 by ELISA in coculture supernatants at 96 h. Data presented are mean ± SEM from a representative experiment. n = 5 mice per group. One- or two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni multiple comparison test (A–G), or unpaired Student’s t test (H–I), *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.