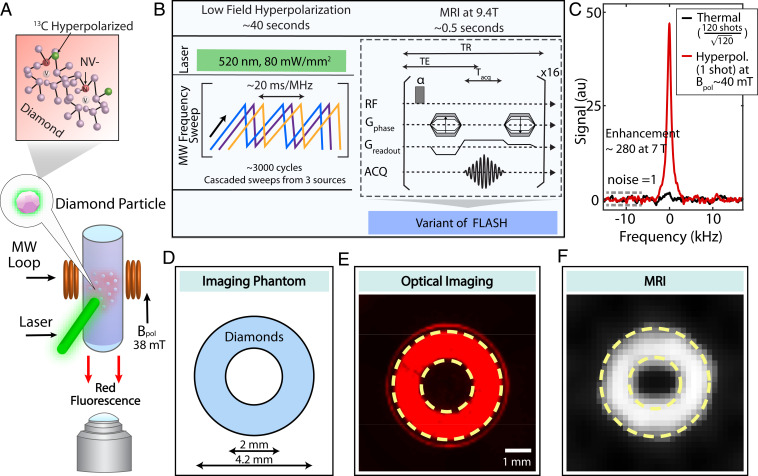
Fig. 1.
Dual-mode optical and MR imaging. (A) Experiment schematic. Diamond particles with centers are imaged with fluorescence under green (520 nm) excitation by a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) detector, as well as under MRI through polarization transferred to lattice nuclei from optically polarized electrons. (B) Hyperpolarization and detection protocol. The DNP occurs at low field 38 mT under MW sweeps across the ESR spectrum. FLASH MR imaging is performed after sample shuttling to 9.4 T. Here echo time TE = 0.5 ms, repetition time TR = 6 ms, acquisition time = 0.36 ms. (C) Typical hyperpolarization signal enhancement, showing signal gain 5 against thermal signal at 7 T, corresponding to 5 orders of magnitude acceleration in MR imaging time. For a fair comparison, the noise in both datasets is normalized to 1 (dashed lines). (D) Ring-shaped phantom filled with 40 mg of 200-m diamond particles employed for dual-mode imaging. (E) Fluorescence image captured through a 630-nm long-pass filter. (F) A MR FLASH image with 16 averages (8 s total imaging time) and a square pixel length of 160 m and square FOV with a 6.4-mm edge.