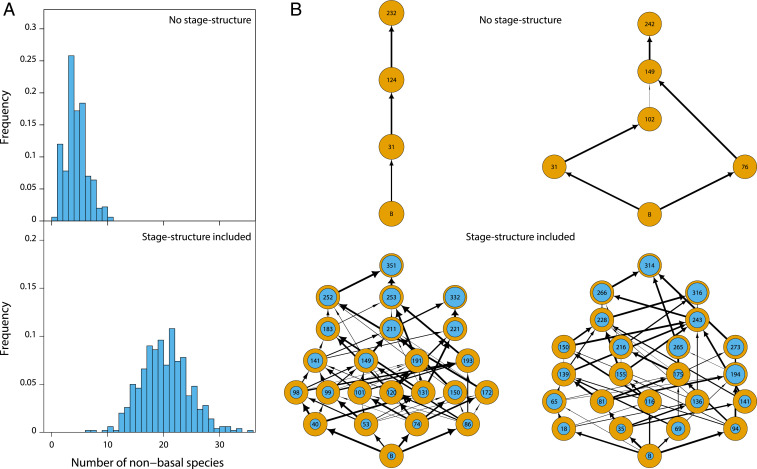
Fig. 2.
Juvenile–adult stage structure increases community size and complexity. (A) Frequency distribution of community sizes (nonbasal species only) and (B) examples of food webs resulting from 500 replicate food web simulations without stage structure (Top) and including stage structure with foraging and predation asymmetry between juveniles and adults (Bottom). In B vertical positions indicate trophic level. Inner circles in Bottom row indicate the density of juveniles as fraction of total population density. Arrow widths indicate the relative feeding preference of consumers for a particular prey species.