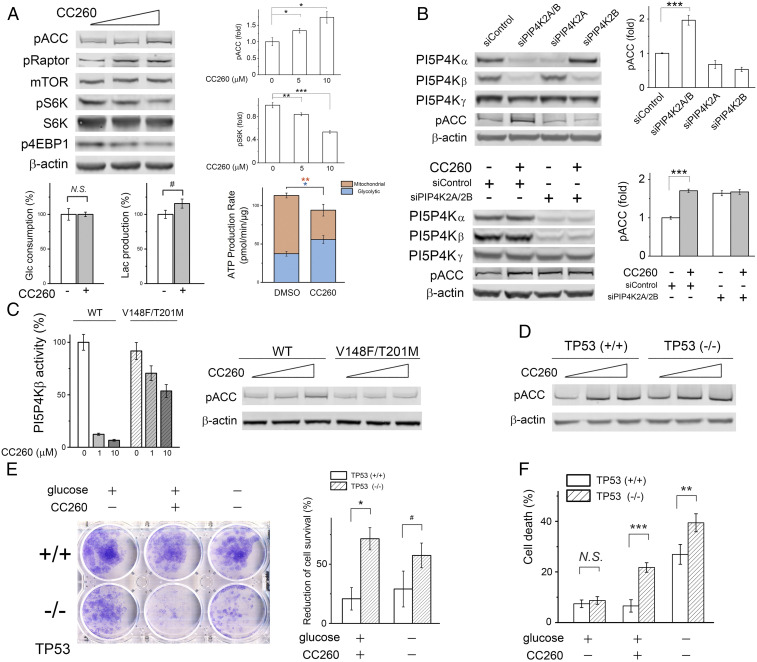
Fig. 5.
PI5P4K inhibition reduces tumor cell survival. (A) CC260 (0, 5, and 10 μM) caused AMPK activation and mTORC1 inhibition in BT474 cells after overnight treatment in DMEM without serum (n = 4). To measure glucose consumption and lactate production, BT474 cells were cultured in DMEM without serum for 24 h (the medium did not contain pyruvate). In DMSO control, glucose concentration decreased by 7.0 mM, and the final lactate concentration was 11.9 mM (∼85% of the consumed glucose was used for lactate fermentation). With 10 μM CC260, glucose decreased by 7.0 mM while lactate accumulated to 13.8 mM (∼99% used for fermentation) (n = 3). Mitochondrial and glycolytic ATP production rates were shown as means ± SEM (n = 16). (B) Simultaneous knockdown of PI5P4Kα and PI5P4Kβ by siRNA caused AMPK activation. Oligo “siControl” is of random sequence. After 1 d of transfection, BT474 cells were transferred to an siRNA-free DMEM with 10% fetal bovine serum and cultured for 2 more days before Western blot analysis (n = 4). CC260 did not cause further AMPK activation when PI5P4Kα and PI5P4Kβ were both knocked down by siRNA (n = 3). After transfection, BT474 cells were treated with 10 μM CC260 overnight before Western blot analysis. (C) AMPK activation was abrogated in BT474 cells expressing a refractory PI5P4Kβ double mutant. Cells were treated with compound (0, 5, and 10 μM) overnight in serum-free DMEM. (Left) Comparing the in vitro activities of wild-type and mutant PI5P4Kβ at different inhibitor concentrations (n = 3). (D) CC260 caused AMPK activation in both p53+/+ and p53−/− MCF-10A cells. (E) CC260 or glucose starvation (12 h) was selectively toxic toward p53−/− cells, causing a greater reduction of the number of proliferative cells in the clonogenic assay. The area covered by the cell was quantified, and the percentage decrease was based on comparison with p53+/+ and p53−/− cells without compound treatment or glucose starvation, respectively (n = 3). (F) After overnight CC260 (10 μM) treatment or glucose starvation in serum-free DMEM/F12 medium supplemented with 0.5 μg/mL hydrocortisone, 100 ng/mL cholera toxin, and 10 μg/mL insulin, the dead cells were measured by propidium iodide staining (n = 6). Results are shown as means ± SEM, * indicates P ≤ 0.01, ** indicates P ≤ 0.001, *** indicates P ≤ 0.0001, and # indicates P ≤ 0.05 based on Student’s t test. N.S., nonstatistically significant.