Figure 1.
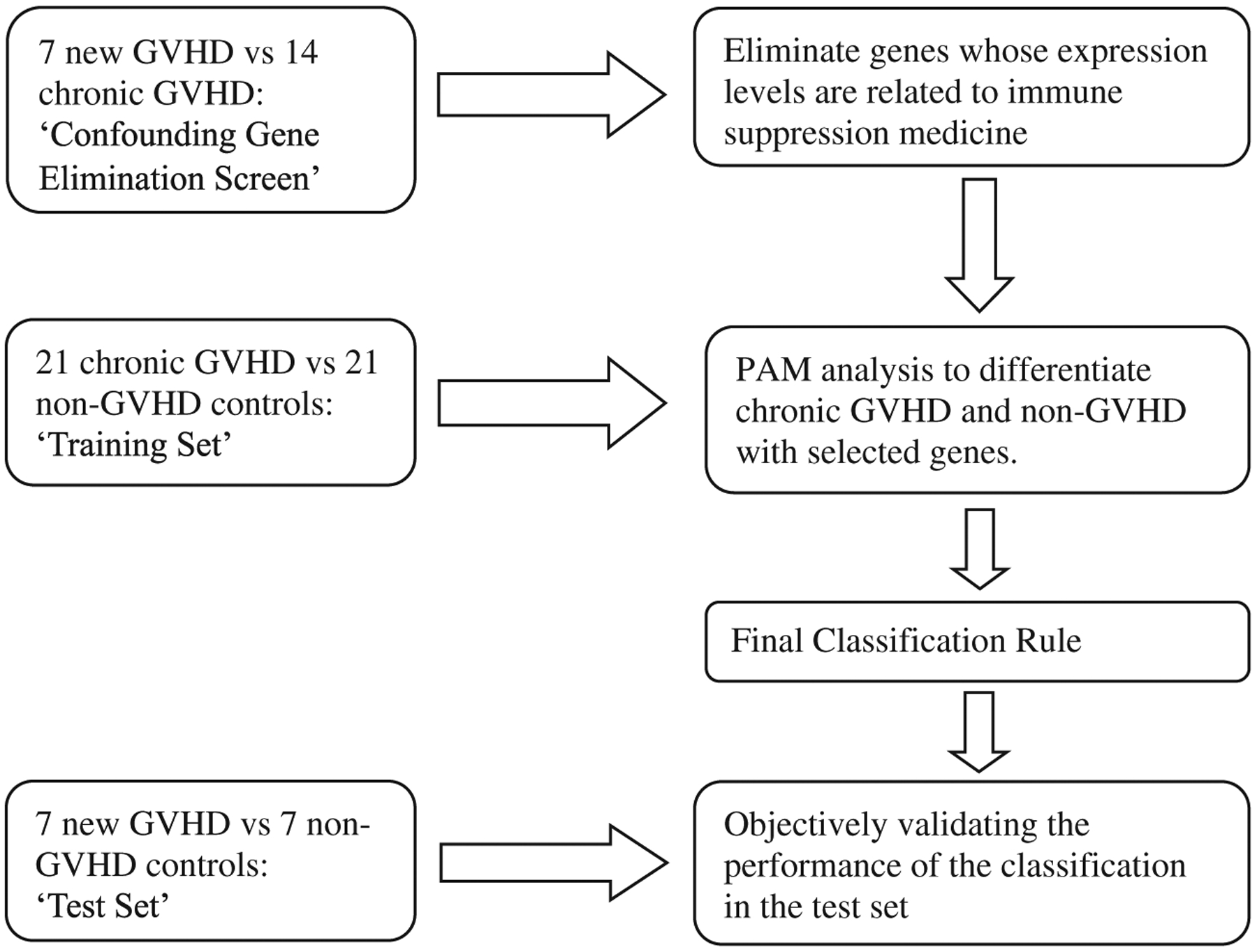
Study design. Retrospective banked samples from 63 patients (35 with chronic GVHD and 28 non-GVHD) and prospectively obtained samples from 7 patients with new onset chronic GVHD satisfied study inclusion and exclusion criteria for gene expression profiling. We constructed three data sets: a ‘confounding gene elimination screen’ set that consisted of the 7 new GVHD patients and 14 chronic GVHD patients; a ‘training set’ that consisted of 21 chronic GVHD patients and 21 non-GVHD controls and a ‘test set’ that consisted of the 7 new GVHD patients and 7 non-GVHD controls. In the confounding gene elimination screen, we compared gene expression levels in patients with GVHD on immune suppression medicine to those not yet on immune suppression medicine and disregarded genes whose t-test statistics were beyond the interval of [−1,1]. In the training set, we applied the PAM method to discriminate GVHD from non-GVHD using the selected probe sets identified from the screening step. We evaluated the performance of the classification rule developed from the training set to differentiate chronic GVHD patients from non-GVHD patients in the test set. We repeated the entire analysis 100 times using different random splits of patient samples in the screening, training and test sets and recorded the frequency of the selected genes from the PAM classifiers to determine reproducibility.
