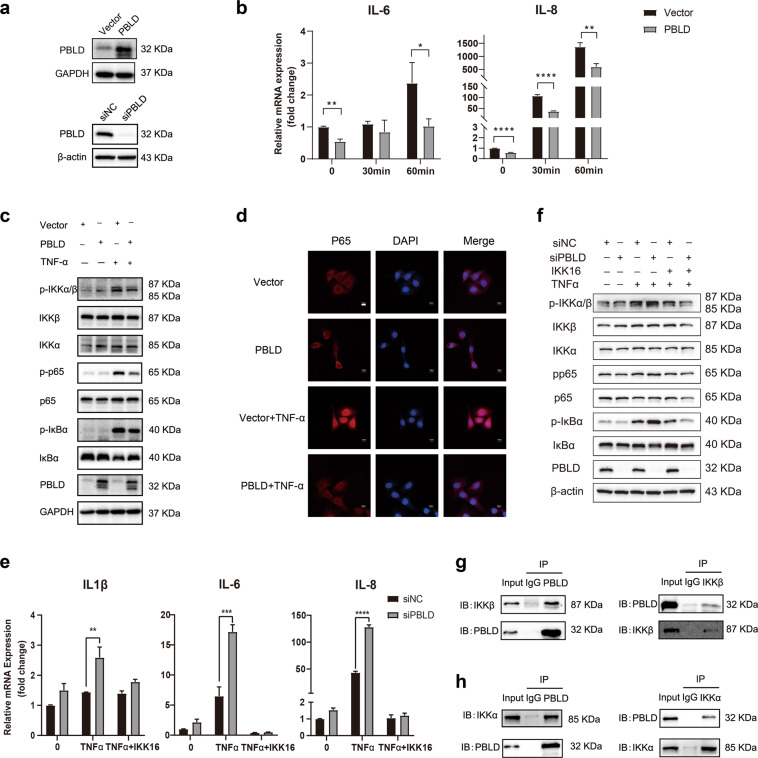
Fig. 7. PBLD suppresses TNF-α-induced inflammatory responses in IECs by inhibiting NF-κB activation.
a Western blot showing the expression of PBLD in a fetal human cell line (FHC) transfected with PBLD-expressing lentivirus (FHC-PBLD) or control lentivirus vector (FHC-vector) (upper) and siNC or siPBLD (lower). b qRT-PCR results showing the production of inflammatory mediators in FHC-vector and FHC-PBLD after TNF-α (10 ng/mL) treatment for the indicated amount of time. Data are mean±standard deviation (SD). **p < 0.01. c Western blot analysis of proteins in FHC-vector and FHC-PBLD cells after TNF-α (10 ng/mL) treatment for 1 hour. d Immunofluorescent staining for p65 in FHC-vector and FHC-PBLD cells after TNF-α (10 ng/mL) treatment for 1 hour. Scale bars: 10 μm. e qRT-PCR analysis of inflammatory mediators production and (f) immunoblot analysis of NF-κB signal pathway in FHC cells transfected with siNC or siPBLD, treated with 5 µM IKK-16 for 2 hours, followed by TNF-α (10 ng/mL) treatment for 1 h. g Immunoblot analysis of IKKβ and PBLD expression in a co-immunoprecipitation assay with anti-PBLD (left) or anti-IKKβ (right) antibodies in FHC-PBLD cells. h Immunoblot analysis of IKKα and PBLD expression in a co-immunoprecipitation assay with anti-PBLD (left) or anti-IKKα (right) antibodies in FHC-PBLD cells.