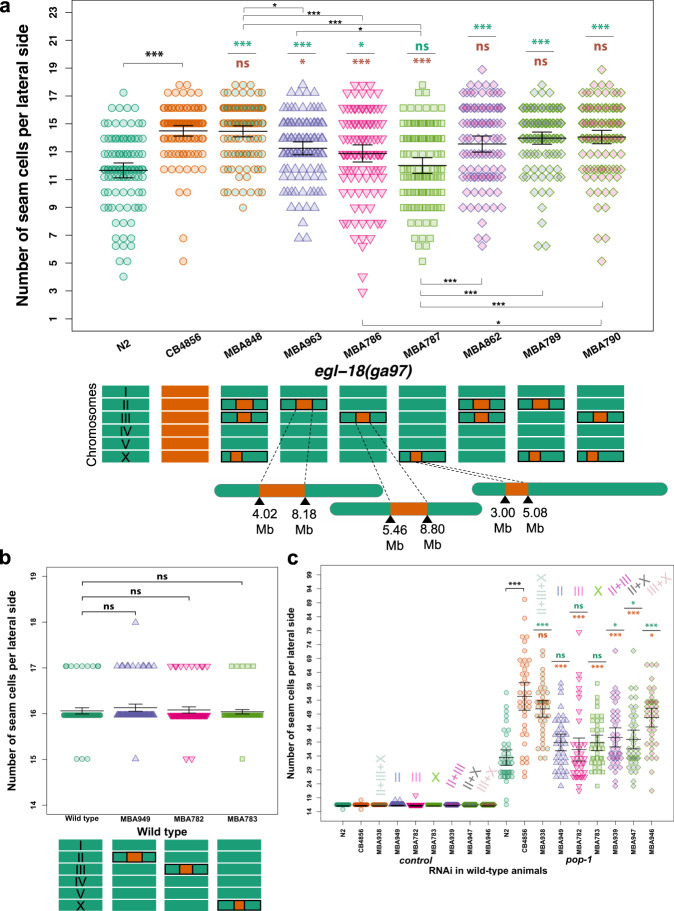
Fig. 4. Phenotypic analysis of near isogenic lines identifies major QTLs.
a Seam cell number in near isogenic lines containing individual and combinations of the identified QTLs from CB4856 into the egl-18(ga97) N2 background. One-way ANOVA showed that SCN was significantly affected by the strain (F (8, 905) = 16.55, p < 2.2 × 10−16, n ≥ 100 independent animals). Stars show significant differences by post hoc Tukey HSD (***p < 0.001 or *p < 0.05). Note that QTLs on chromosomes II and III, but not on the X, were sufficient to increase seam cell number in the egl-18(ga97) mutant in the N2 background. Cartoon of chromosomes below the graph depict the genotype of the strain. b SCN counts in near isogenic lines containing individual QTLs in a wild-type background. One-way ANOVA shows no statistically significant differences in SCN of NILs compared with wild-type with no QTLs (F (3, 396) = 1.34, p = 0.26, n = 100 independent animals). c pop-1 RNAi in near isogenic lines in a wild-type background containing individual and combinations of the identified QTLs. The same colour code is used as in a to define different combinations of QTLs. A significant effect of strain was found on SCN upon pop-1 RNAi using one-way ANOVA (F (8, 351) = 17.85, p < 2.2 × 10−16, n = 40 independent animals). Error bars in a–c indicate 95% confidence intervals around the mean. Comparisons against N2 and CB4856 are shown with green and orange stars, respectively, in a and c and represent p values by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (*** p < 0.001 or * p < 0.05). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.