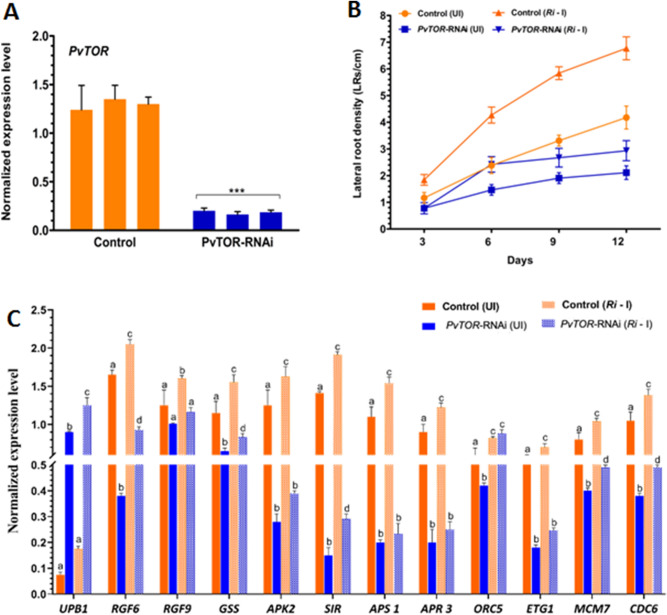
Figure 3.
Knockdown of PvTOR inhibits AM fungus-stimulated lateral root production and downregulates the expression of root meristem regulatory genes in P. vulgaris. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of PvTOR transcript levels in control (empty vector) and PvTOR-RNAi roots at 10 days post emergence. Each bar represents three individual transformants (representative RNAi plant 1, 2, and 3). (B) Lateral root density in uninoculated and Ri-inoculated transgenic roots of control and PvTOR-RNAi at the indicated time points. (C) RT-qPCR analysis of the transcript levels of root meristem regulatory genes such as UPB1, RGF6, RGF9, GSS, APK2, SIR, APS1, APR3, ORC5, ETG1, MCM7, and CDC6 in control and PvTOR-RNAi transgenic roots at 6 dpi with Ri. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed on cDNA of root meristem RNA samples. Transcript accumulation was normalized to the expression of EIF4a and IDE, which were used as reference genes. For A, an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test was used to assess statistical significance (***P < 0.001). For B, the statistical significance of differences was determined using Tukey’s test followed by two-way ANOVA the results were statistically significant at p < 0.05 except for the Control (UI) vs. PvTOR-RNAi (UI), Control (UI) vs. PvTOR-RNAi (Ri—I), PvTOR-RNAi (UI) vs. PvTOR-RNAi (Ri—I) at 3 day samples and Control (UI) vs. PvTOR-RNAi (Ri—I) at 6 day samples. For D, Tukey’s test followed by two-way ANOVA was used to asses statistical significance and the mean values of each gene with unlike letters were significantly different (P < 0.05). Error bars refer to the SD of the mean of three biological replicates (n > 9 for A & D, n > 30 for B). Ri, R. irregularis.