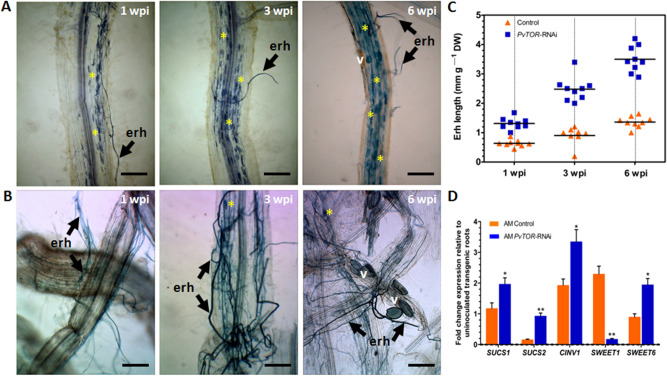
Figure 4.
Arbuscular mycorrhizal extraradical hyphae in P. vulgaris PvTOR-RNAi roots. (A–B) Transgenic root surface showing extraradical hyphae of mycorrhiza in control (A) and PvTOR-RNAi (B) plants at 1, 3, and 6 week(s) post inoculation (wpi) with R. irregularis. Arbuscule containing cells are indicated with an asterisk. erh, extraradical hyphae; v, vesicle. Bars = 2 mm. (C) Length of arbuscular mycorrhizal extraradical hyphae relative to the dry weight of transgenic roots at 1, 3, and 6 wpi with R. irregularis. n = 9 plants per time point for each line (AM control and AM PvTOR-RNAi). (D) RT-qPCR analysis of the transcript levels of sugar metabolism and sucrose transport genes in control and PvTOR-RNAi transgenic roots at 1 wpi with R. irregularis. Data are the fold-change expression relative to uninoculated transgenic roots. Transcript accumulation was normalized to the expression of EIF4a and IDE, which were used as reference genes. The statistical significance of differences between AM control and AM PvTOR-RNAi roots was determined using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). Error bars refer to the SD of the mean of three biological replicates.