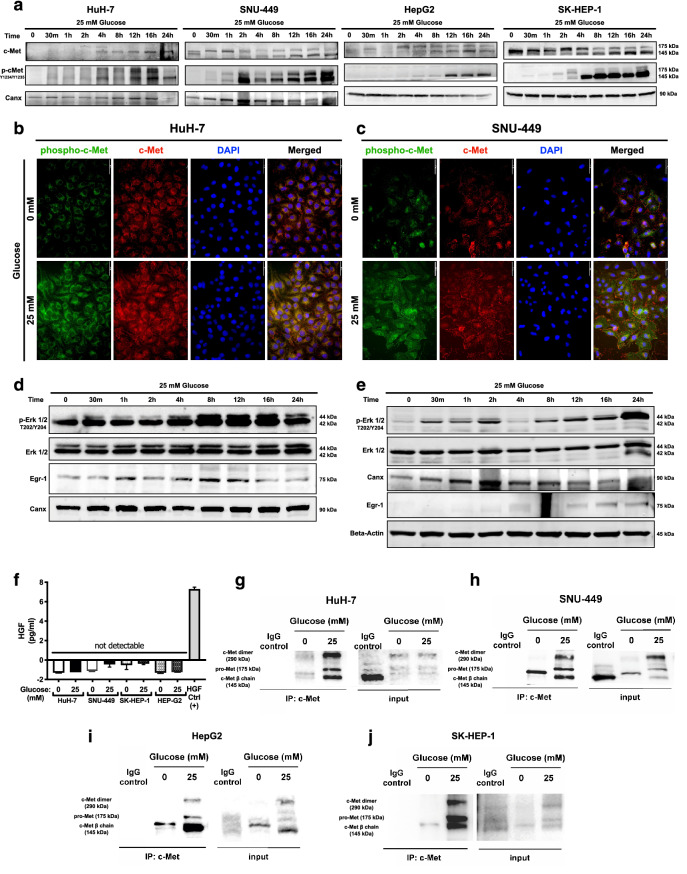
Figure 3.
High glucose exposure activated c-Met and downstream signaling via promoting ligand-independent homodimerization. (a) Immunoblotting of time-dependent c-Met protein expression and activation phosphorylations (Y1234/Y1235) in response to high glucose treatment in HuH-7, HepG2, SNU-449, and SK-HEP-1 cells. Immunofluorescence imaging of Alexa-594-labeled c-Met protein and Alexa-488 labeled c-Met activation phosphorylations (Y1234/Y1235) in response to no- and high-glucose (25 mM) conditions in (b) HuH-7 and (c) SNU-499 cells. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI staining. Immunoblotting of time-dependent expressions of Erk1/2 activation phosphorylations (T202/Y204), Erk1/2 total protein and Egr-1 protein in response to high glucose stimulation in (d) HuH-7 and (e) SNU-449 cells. Calnexin (Canx) immunoblotting performed as an internal control. (f) Graphical presentation of HGF secretion analysis with ELISA. Conditioned media of HCC cells cultured in no- and high-glucose supplemented conditions were analyzed with sandwich ELISA. Crosslinking-immunoprecipitation assay for analyzing c-Met homodimerization under no- and high-glucose (25 mM) conditions in (g) HuH-7, (h) SNU-449, (i) HepG2 and (j) SK-HEP-1 cells. After starvation and indicated treatments for 16 h, proteins were crosslinked with Sulfo-EGS, c-Met was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with c-Met targeting primary antibody. Full length blots are presented in Supplementary. Column graph was generated using GraphPad Prism version 8.2.1 for MacOS, GraphPad Software, San Diego, California USA, https://www.graphpad.com.