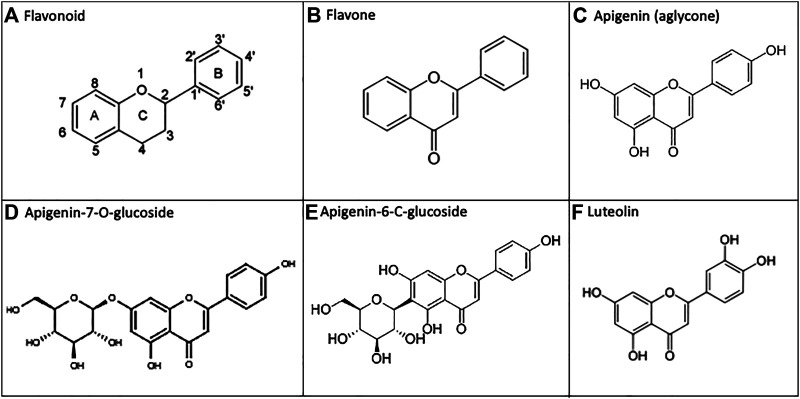
FIGURE 1.
Apigenin and related chemical structures. (A) General flavonoid structure as 15-carbon molecules containing two phenyl groups and a heterocyclic carbon ring. (B) The flavone sub-class of flavonoids have a C2-C3 double bond, unsubstituted C3 carbon, and a C4 ketone oxidization. (C) Apigenin is a 4′, 5, 7-trihydroxyflavone. (D, E) In nature, apigenin is commonly found as a 7-O-glucoside, 6-C-glucoside or 8-C-glucoside, which is enzymatically metabolized to free apigenin prior to intestinal absorption. F) Apigenin undergoes phase I metabolism via CYP1A2, and to a lesser extent CYP3A4, generating the 3′-hydroxylated product luteolin.