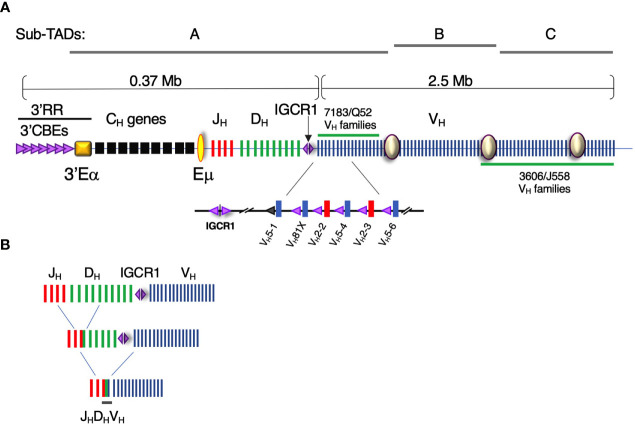
Figure 1.
The Igh locus contains ~100 VH gene segments over an almost 3Mb genomic interval. (A) (Upper panel) Diagram of the Igh locus indicating VH, D, JH, and CH exons and regulatory elements (not to scale). The intronic Eμ and 3′Eα super-enhancers and intergenic control region 1 (IGCR1), composed of two divergent CBEs, are critical regulatory elements. CBE orientation is indicated by (purple) triangle direction. The 3′ regulatory region (3′RR) is a composite of nine CBEs located at the 3′ boundary of the Igh locus adjacent to 3′Eα super-enhancer. Sites I, II, and III (purple circles) anchor the sub-topologically associating domain (Sub-TADs) A, B, and C. The VHS107 family along with nine smaller VH families comprise the intermediate VH segments. The interspersed distal VH gene segments are composed of the VHJ558 and VH3609 families and are located at the 5’ end of the locus. (Lower panel) The VH7183 (blue bars) and VHQ52 families (red bars) are located at the DHJH-proximal end of the locus. Each DHJH -proximal VH exon is paired with a recombination signal sequence (not shown) and a CBE (purple triangle). The CBE associated with VH5-1 exon is non-functional (gray triangle). VH81X (VH5-2) is the second VH exon gene relative to IGCR1. (B) Schematic of the stepwise process of V(D)J recombination. DH-JH rearrangement precedes VH-DHJH recombination.