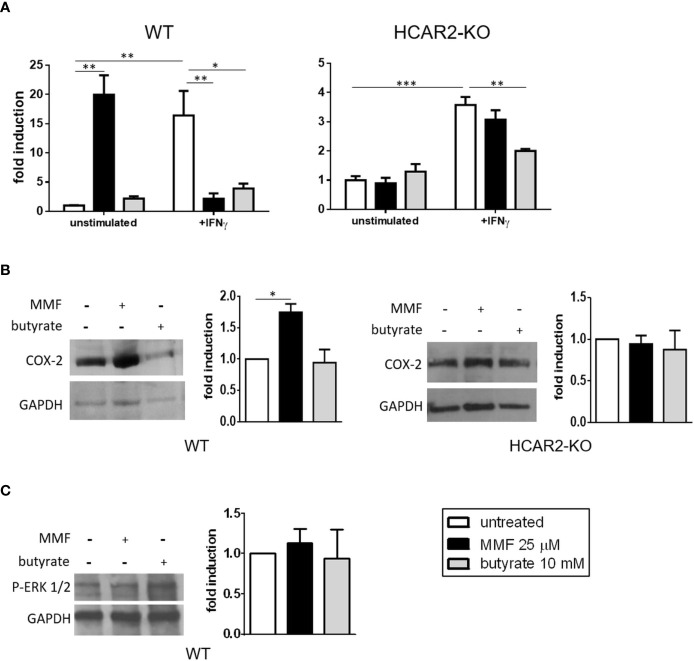
Figure 2.
Under non-inflammatory conditions, MMF signals through the HCAR2/COX-2 pathway to increase the mRNA expression of the pro-inflammatory Tnf in IEC. (A) MMF differentially affects Tnf expression in IEC under different conditions of activation. Tnf mRNA expression in IEC isolated from WT (left panel) or HCAR2-KO (right panel) mice and activated or not with IFNγ (100 ng/ml), in presence or absence of MMF or butyrate for 6 h. (B) MMF, but not butyrate, induces COX-2 in unstimulated IEC, via HCAR2. Western blotting for COX-2 in IEC isolated from WT (left panels) and HCAR2-KO (right panels) mice treated or not with MMF or butyrate for 6 h. (C) MMF does not activate HCAR2/ERK1/2 pathway in unstimulated IEC. Western blotting for P-ERK1/2 in IEC isolated from WT mice treated or not with MMF or butyrate for 6 h. Representative blots and densitometric quantification graphs are shown. Real-time PCR data are presented as fold induction over the expression of the gene in untreated cells. GAPDH was assessed as loading control for Western blotting and quantification by densitometric analysis of bands is presented as COX-2 over GAPDH (B) or p-ERK1/2 over GAPDH (C). All results are shown as mean ± SEM of at least N = 3 experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.