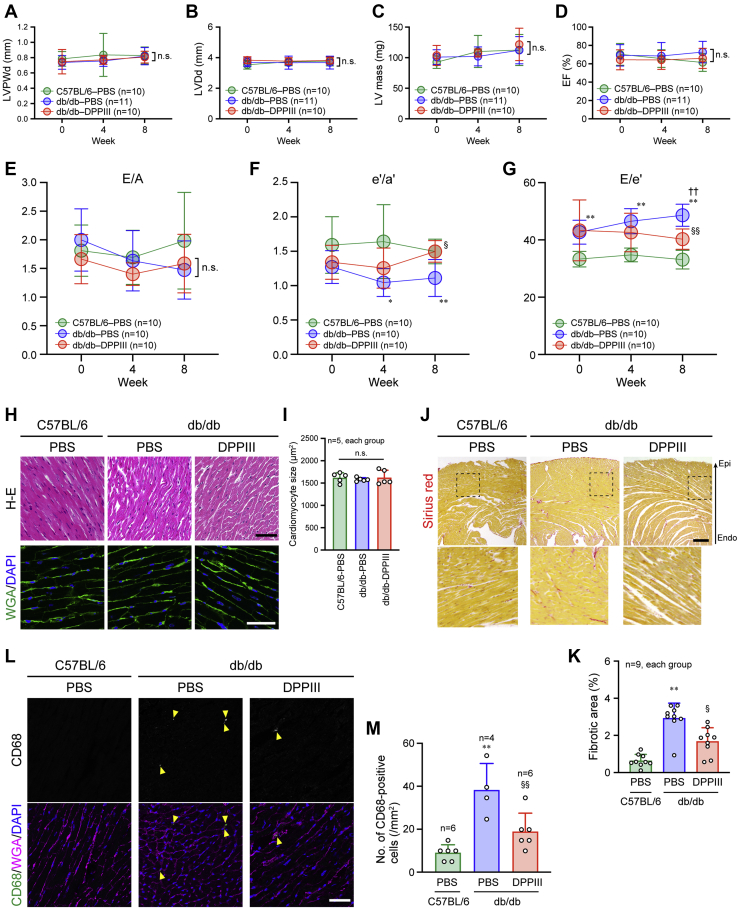
Figure 1.
Cardioprotective effect of DPPIII on diabetic mice.A–G, echocardiographic measurement of each parameter analyzed every 4 weeks during the 8-weeks experimental period. H, hematoxylin-eosin (H-E) and WGA staining of the mouse heart after the 8-week treatment. I, summary graph of cardiomyocyte size measured by WGA staining. J, cardiac fibrosis detected by Sirius red staining after the 8-week treatment. The dotted square was enlarged and shown below. K, summary graph of the percentage of fibrotic areas in the cardiac sections. L, confocal images of CD68 immunostaining. Cell membrane and nuclei were counterstained with WGA and DAPI, respectively. M, summary graph of the number of CD68-positive cells. Scale bars: 50 μm (H and L) and 200 μm (J). In A–G, two-way ANOVA was applied for comparing the data between groups, and one-way ANOVA was applied for comparing the results at week 0 with those at other time points; in I, K, and M, one-way ANOVA was used to compare the data of each group. ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 versus C57BL/6 mice; ††p < 0.01 versus 0 weeks; §p < 0.05 and §§p < 0.01 versus PBS-infused db/db mice. e'/a', ratio of early to atrial diastolic mitral annular velocities; E/e', ratio of peak transmitral velocity of early inflow to early diastolic mitral annular velocity; E/A, ratio of peak transmitral velocity of early inflow to atrial inflow; EF, ejection fraction; LVDd, LV diastolic diameter; LVPWd, left ventricular posterior wall diastolic thickness.