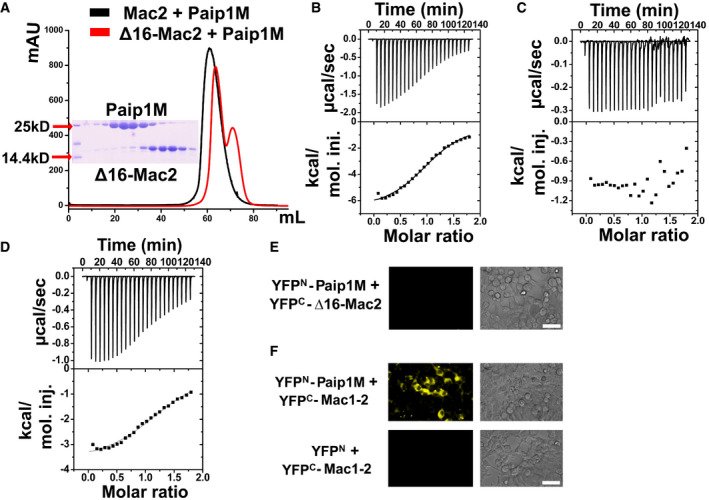
Figure 3. The N‐terminal 16 residues of Mac2 are important for Paip1M binding and Mac1 does not affect Mac2:Paip1 interaction.
-
AThe Mac2 and Paip1M interaction was impaired by removing the N‐terminal 16 residues as revealed by the gel filtration assay.
-
BIsothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) assay of Mac2 binding Paip1M. The raw calorimetric curve is displayed on top while the fitted binding isotherm curve is at the bottom. The measured values are as follows: N = 0.94 ± 0.01 (binding stoichiometry); K d = 15.5 ± 1.5 μM (dissociation constant); ΔH = −6,778 ± 149 cal/mol (standard molar enthalpy change for binding); ΔS = −0.716 cal/mol/K (standard molar entropy change).
-
CΔ16‐Mac2 lost all binding affinity to Paip1M in the ITC experiment.
-
DITC result of Mac1–2 interacting with Paip1M. The experimental results are as follows: N = 1.14 ± 0.02; K d = 18.6 ± 2.5 μM; ΔH = −3,730 ± 100 cal/mol; ΔS = 9.14 cal/mol/K.
-
E, FΔ16‐Mac2 cannot bind Paip1M, Mac1–2 binds to Paip1M in the split‐YFP assay. Scale bars represent 50 µm.
