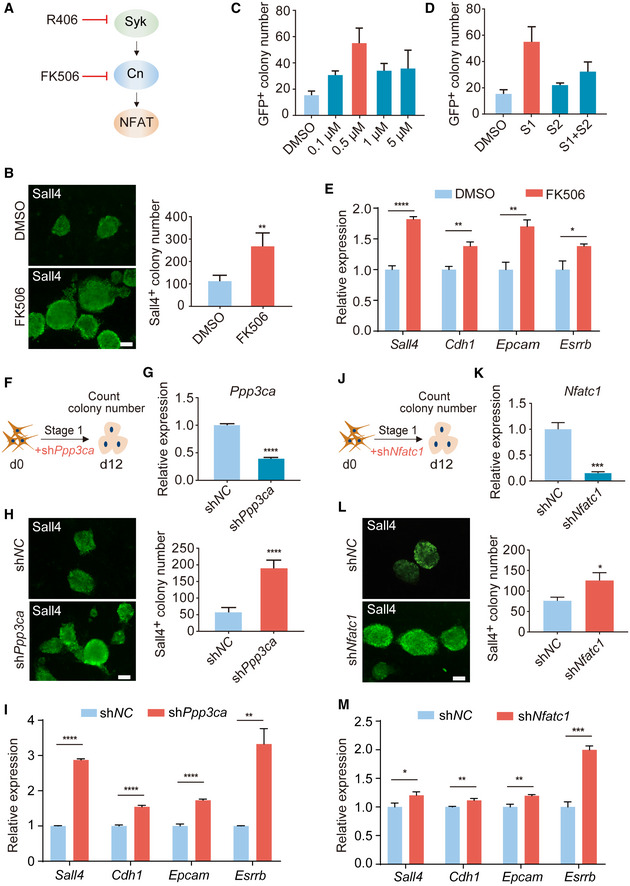
Figure 2. Inhibition of Syk‐Cn‐NFAT signaling pathway promotes chemical reprogramming.
-
ASchematic diagram showing Syk‐Cn‐NFAT pathway axis.
-
BImmunofluorescence of Sall4 in reprogramming intermediates treated with DMSO and FK506. n = 5. Scale bar, 100 μm.
-
C, DConcentration (C) and stage (D) test of FK506 during reprogramming. n = 3.
-
ERT–qPCR analysis of Sall4, Cdh1, Epcam, and Esrrb gene expression in reprogramming intermediates treated with DMSO and FK506. n = 3.
-
FDiagram showing the procedure of Ppp3ca knockdown at the early stage of reprogramming.
-
GRT–qPCR analysis of Ppp3ca expression in MEFs infected with shNC and shPpp3ca viruses. n = 3.
-
HImmunofluorescence of Sall4 in WT cells and Ppp3ca knockdown cells on d12. n = 6. Scale bar, 100 μm.
-
IRT–qPCR analysis of pluripotent genes expression in cells treated with shNC and shPpp3ca. n = 3.
-
JDiagram showing the procedure of shNfatc1 virus infection at the early stage of reprogramming.
-
KRT–qPCR analysis of Nfatc1 expression in MEFs infected with shNC and shNfatc1 viruses. n = 3.
-
LImmunofluorescence of Sall4 in WT cells and Nfatc1 knockdown cells on d12. n = 3. Scale bar, 100 μm.
-
MRT–qPCR analysis of pluripotent genes expression in cells treated with shNC and shNfatc1. n = 3.
Data information: All data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was assessed by the two‐tailed Student’s t‐test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. See also Fig EV2.
